C-kit signaling promotes human pre-implantation 3PN embryonic development and blastocyst formation
- PMID: 31506068
- PMCID: PMC6737624
- DOI: 10.1186/s12958-019-0521-8
C-kit signaling promotes human pre-implantation 3PN embryonic development and blastocyst formation
Abstract
Background: Although in vitro culture system has been optimized in the past few decades, the problem of few or no high quality embryos has been still not completely solved. Accordingly, fully understanding the regulatory mechanism of pre-implantation embryonic development would be beneficial to further optimize the in vitro embryo culture system. Recent studies have found the expression of c-kit in mouse embryo and its promotion effects on mouse embryonic development. However, it is unclear the expression, the role and the related molecular regulatory mechanism of c-kit in human pre-implantation embryo development. Therefore, the present study is to determine whether c-kit is expressed in human pre-implantation embryos, and to investigate the possible regulatory mechanism of c-kit signaling in the process of embryonic development.
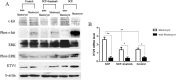
Methods: The present study includes human immature oocytes and three pronucleus (3PN) embryos collected from 768 women (28-32 ages) undergoing IVF, and normal 2PN embryos collected from ICR mice. Samples were distributed randomly into three different experimental groups: SCF group: G-1™ (medium for culture of embryos from the pro-nucleate stage to day 3) or G-2™ (medium for culture of embryos from day3 to blastocyst stage) + HSA (Human serum album) solution + rhSCF; SCF + imanitib (c-kit inhibitor) group: G-1™ or G-2™ + HSA solution + rhSCF + imanitib; SCF + U0126 (MEK/ERK inhibitor) group: G-1™ or G-2™ + HSA solution + rhSCF + U0126; Control group: G-1™ or G-2™ + HSA solution + PBS; The rate of good quality embryos at day 3, blastulation at day 6 and good quality blastulation at day 6 were analysis. RT-PCR, western blot and immunofluorescence staining were applied to detect the target genes and proteins in samples collected from human or mice, respectively.
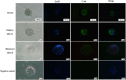
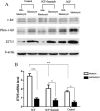
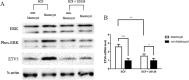
Results: c-kit was expressed ubiquitously in all human immature oocytes, 3PN embryos and 3PN blastocysts. In the experiment of human 3PN embryos, compared with other groups, SCF group showed obviously higher rate of good quality at day 3, better rate of blastocyst formation at day 6 and higher rate of good quality blastocyst formation at day 6. Furthermore, we observed a higher ETV5 expression in SCF group than that in other groups. Similar results were also found in animal experiment. Interestingly, we also found a higher phosphorylation level of MEK/ERK signal molecule in mice embryos from SCF group than those from other groups. Moreover, inhibition of MEK/ERK signaling would remarkably impeded the mice embryonic development, which might be due to the reduced ETV5 expression.
Conclusions: The present study firstly revealed that c-kit signaling might promote the human pre-implantation embryonic development and blastocyst formation by up-regulating the expression of ETV5 via MEK/ERK pathway. Our findings provide a new idea for optimizing the in vitro embryo culture condition during ART program, which is beneficial to obtain high quality embryos for infertile patients.
Keywords: C-kit; ETV5; Embryonic development; IVF; In vitro culture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differences in gene expression profiles between human preimplantation embryos cultured in two different IVF culture media.Hum Reprod. 2015 Oct;30(10):2303-11. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dev179. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Hum Reprod. 2015. PMID: 26202924 Clinical Trial.
-
Paternal influence of sperm DNA integrity on early embryonic development.Hum Reprod. 2014 Nov;29(11):2402-12. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deu228. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Hum Reprod. 2014. PMID: 25205757
-
Stem cell factor/c-Kit signaling in in vitro cultures supports early mouse embryonic development by accelerating proliferation via a mechanism involving Akt-downstream genes.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2010 Nov;27(11):619-27. doi: 10.1007/s10815-010-9449-9. Epub 2010 Jun 30. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2010. PMID: 20589425 Free PMC article.
-
Should extended blastocyst culture include Day 7?Hum Reprod. 2018 Jun 1;33(6):991-997. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dey091. Hum Reprod. 2018. PMID: 29648640 Review.
-
Time-lapse monitoring technologies for the selection of bovine in vitro fertilized embryos with high implantation potential.J Reprod Dev. 2023 Apr 3;69(2):57-64. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2022-131. Epub 2023 Feb 12. J Reprod Dev. 2023. PMID: 36775299 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of stem cell factor in follicular fluid and granulosa cells on oocyte maturity and clinical pregnancy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 29;102(52):e36749. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036749. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38206705 Free PMC article.
-
GnRH antagonist weakens endometrial stromal cells growth ability by decreasing c-kit receptor expression.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022 Feb 4;20(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12958-021-00886-y. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35120552 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell factor's role in enhancing the quality of fertilized and cloned porcine embryos for improved embryonic stem cell derivation.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Nov 16;10:1285530. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1285530. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38033636 Free PMC article.
-
Coenzyme Q10 Stimulate Reproductive Vatality.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Aug 30;17:2623-2637. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S386974. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 37667786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SWI/SNF ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complex in cell lineage priming and early development.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Apr 24;52(2):603-616. doi: 10.1042/BST20230416. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38572912 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81960288/National Natural Science Foundation of China (CN)
- 81960271/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20192BBGL70005/Jiangxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology
- 20171BAB215013/Jiangxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology
- 20185393/the Science and Technology Program of Health Commission of Jiangxi Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

