[Correlation between Mycoplasma pneumoniae DNA replication level and disease severity in children with severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia]
- PMID: 31506145
- PMCID: PMC7390246
- DOI: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2019.09.006
[Correlation between Mycoplasma pneumoniae DNA replication level and disease severity in children with severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia]
Abstract
Objective: To study the correlation of Mycoplasma pneumoniae DNA (MP-DNA) replication level in throat swab and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) with disease severity in children with severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (SMPP).
Methods: A total of 44 children with SMPP who underwent bronchoalveolar lavage were enrolled as subjects. The serum levels of cytokines and MP-DNA replication times in throat swab were measured in the acute stage and the recovery stage, and the levels of interleukin (IL)-8 and MP-DNA replication times in BALF were measured in the acute stage. According to whether mechanical ventilation was needed for respiratory failure, the children were divided into a mechanical ventilation group (n=19) and a non-mechanical ventilation group (n=25), and the two groups were compared in MP-DNA replication times in BALF.
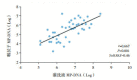
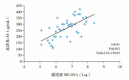
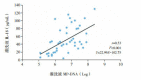
Results: For the children with SMPP, serum levels of C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, lactate dehydrogenase, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-18 in the acute stage were significantly higher than those in the recovery stage (P<0.05). In the acute stage, MP-DNA replication times in throat swab were positively correlated with those in BALF (r=0.613, P<0.05), and MP-DNA replication times in BALF were positively correlated with IL-18 levels in peripheral blood and BALF (r=0.613 and 0.41 respectively, P<0.05). Compared with the non-mechanical ventilation group, the mechanical ventilation group had significantly higher MP-DNA replication times in BALF, a significantly longer duration of systemic hormone treatment, significantly higher serum levels of lactate dehydrogenase and IL-18, and significantly higher white blood cell count and IL-18 level in BALF (P<0.05).
Conclusions: In children with SMPP, MP-DNA replication level in throat swab and BALF can be used as a reference index for the assessment of disease severity.
目的: 探讨重症肺炎支原体肺炎(SMPP)患儿咽拭子、肺泡灌洗液(BALF)中肺炎支原体DNA(MP-DNA)复制水平与病情的相关性。
方法: 44例行支气管肺泡灌洗术的SMPP患儿为研究对象,分别在急性期和恢复期检测相关血清细胞因子水平及咽拭子MP-DNA复制倍数,并检测急性期BALF中白细胞介素(IL)-18水平及MP-DNA复制倍数。并按照病程中是否出现呼吸衰竭需要机械通气分为机械通气组(n=19)与非机械通气组(n=25),比较两组患儿肺泡灌洗液中MP-DNA复制倍数。
结果: 与恢复期相比,SMPP患儿在急性期时,血清C反应蛋白、红细胞沉降率、乳酸脱氢酶、IL-1、IL-6、IL-8、IL-18水平显著增高(P < 0.05)。急性期咽拭子与BALF的MP-DNA复制倍数呈显著正相关(r=0.613,P < 0.05);BALF中MP-DNA复制倍数与外周血及BALF的IL-18水平呈正相关(分别r=0.613、0.41,均P < 0.05)。机械通气组BALF中MP-DNA复制倍数高于非机械通气组,且全身激素治疗时间明显长于非机械通气组,血清乳酸脱氢酶、IL-18及BALF中WBC总数、IL-18水平也更高(P < 0.05)。
结论: SMPP患儿急性期咽拭子与BALF MP-DNA复制水平可作为病情评估的参考。
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of cytokine levels, cytological findings, and MP-DNA level in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 May;11(5):e849. doi: 10.1002/iid3.849. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 37249293 Free PMC article.
-
[Correlation between galectin-3 level in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and cellular immunity in children with refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Feb;21(2):150-154. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2019.02.008. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30782277 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
High Mycoplasma pneumoniae loads and persistent long-term Mycoplasma pneumoniae DNA in lower airway associated with severity of pediatric Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Dec 10;19(1):1045. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4667-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31823740 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines and refractory mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children: a systematic review.Minerva Pediatr (Torino). 2024 Apr;76(2):259-267. doi: 10.23736/S2724-5276.23.07158-6. Epub 2023 May 8. Minerva Pediatr (Torino). 2024. PMID: 37155205
-
[Analysis of 3 cases with Mycoplasma pneumoniae-associated hemophagocytic syndrome and review of literature].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Oct;52(10):792-6. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25537549 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Identification and Characterization of Nasal Polyposis and Mycoplasma Superinfection by Scanning Electron Microscopy and Nasal Cytology with Optical Microscopy: A Case Report.Diagnostics (Basel). 2019 Nov 4;9(4):174. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics9040174. Diagnostics (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31689994 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of cytokine levels, cytological findings, and MP-DNA level in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 May;11(5):e849. doi: 10.1002/iid3.849. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 37249293 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of measuring MP-DNA, C-reactive protein, and inflammatory cytokines in children with mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Feb 15;16(2):577-583. doi: 10.62347/VCVW7593. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38463592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 戴 瑞, 刘 亢亢, 牛 曼曼, et al. 儿童难治性支原体肺炎86例分析. 临床肺科杂志. 2017;22(1):96–98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6663.2017.01.027. - DOI
-
- 谭 政, 杨 菁菁, 许 小毛, et al. 支原体肺炎合并ARDS 2例并文献复习. 国际呼吸杂志. 2017;37(6):411–417. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-436X.2017.06.003. - DOI
-
- 张 慧芬, 白 海涛, 李 基明, et al. 肺炎支原体肺炎患儿肺炎支原体耐药性与DNA载量和基因型的关系研究. http://www.zgddek.com/CN/abstract/abstract14404.shtml 中国当代儿科杂志. 2017;19(11):1180–1184. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2017.11.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- 宋 宪蓉, 杜 宇哲. 糖皮质激素在儿童难治性肺炎支原体肺炎中的研究. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgywylc201706045 中国药物与临床. 2017;17(6):888–890.
-
- 郑 茂, 陈 瑶, 符 佳, et al. 难治性肺炎支原体肺炎患儿的早期临床特征及相关细胞因子水平变化. 中国医药. 2017;12(10):1499–1502. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4777.2017.10.015. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous