Sonic hedgehog enhances calcium oscillations in hippocampal astrocytes
- PMID: 31506300
- PMCID: PMC6827318
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007883
Sonic hedgehog enhances calcium oscillations in hippocampal astrocytes
Abstract
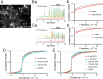
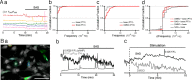
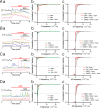
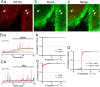
Sonic hedgehog (SHH) is important for organogenesis during development. Recent studies have indicated that SHH is also involved in the proliferation and transformation of astrocytes to the reactive phenotype. However, the mechanisms underlying these are unknown. Involvement of SHH signaling in calcium (Ca) signaling has not been extensively studied. Here, we report that SHH and Smoothened agonist (SAG), an activator of the signaling receptor Smoothened (SMO) in the SHH pathway, activate Ca oscillations in cultured murine hippocampal astrocytes. The response was rapid, on a minute time scale, indicating a noncanonical pathway activity. Pertussis toxin blocked the SAG effect, indicating an involvement of a Gi coupled to SMO. Depletion of extracellular ATP by apyrase, an ATP-degrading enzyme, inhibited the SAG-mediated activation of Ca oscillations. These results indicate that SAG increases extracellular ATP levels by activating ATP release from astrocytes, resulting in Ca oscillation activation. We hypothesize that SHH activates SMO-coupled Gi in astrocytes, causing ATP release and activation of Gq/11-coupled P2 receptors on the same cell or surrounding astrocytes. Transcription factor activities are often modulated by Ca patterns; therefore, SHH signaling may trigger changes in astrocytes by activating Ca oscillations. This enhancement of Ca oscillations by SHH signaling may occur in astrocytes in the brain in vivo because we also observed it in hippocampal brain slices. In summary, SHH and SAG enhance Ca oscillations in hippocampal astrocytes, Gi mediates SAG-induced Ca oscillations downstream of SMO, and ATP-permeable channels may promote the ATP release that activates Ca oscillations in astrocytes.
Keywords: ATP; Sonic hedgehog (SHH); astrocyte; calcium imaging; calcium intracellular release.
© 2019 Adachi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dendrosomatic Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Hippocampal Neurons Regulates Axon Elongation.J Neurosci. 2015 Dec 9;35(49):16126-41. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1360-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26658865 Free PMC article.
-
Hypomorphic Smo mutant with inefficient ciliary enrichment disrupts the highest level of vertebrate Hedgehog response.Dev Biol. 2018 May 15;437(2):152-162. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.03.019. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29571613 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of Cullin3 gene expression enhances the improved effects of sonic hedgehog signaling activation for hypertension and attenuates the dysfunction of vascular smooth muscle cells.Biomed Eng Online. 2022 Jun 17;21(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12938-022-01002-w. Biomed Eng Online. 2022. PMID: 35715796 Free PMC article.
-
Small-molecule modulators of the Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway.Mol Biosyst. 2010 Jan;6(1):44-54. doi: 10.1039/b910196a. Epub 2009 Aug 27. Mol Biosyst. 2010. PMID: 20024066 Review.
-
Roles of astrocytic sonic hedgehog production and its signal for regulation of the blood-brain barrier permeability.Vitam Horm. 2024;126:97-111. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2024.04.006. Epub 2024 May 19. Vitam Horm. 2024. PMID: 39029978 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of sonic hedgehog signaling pathway in the regulation of ion channels: focus on its association with cardio-cerebrovascular diseases.J Physiol Biochem. 2023 Nov;79(4):719-730. doi: 10.1007/s13105-023-00982-0. Epub 2023 Sep 7. J Physiol Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37676576 Review.
-
Development of the observation of membrane fusion with label-free liposomes by calcium imaging.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023 May 17;34:101483. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2023.101483. eCollection 2023 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023. PMID: 37250982 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging principles of primary cilia dynamics in controlling tissue organization and function.EMBO J. 2023 Nov 2;42(21):e113891. doi: 10.15252/embj.2023113891. Epub 2023 Sep 25. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 37743763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytoneme delivery of Sonic Hedgehog from ligand-producing cells requires Myosin 10 and a Dispatched-BOC/CDON co-receptor complex.Elife. 2021 Feb 11;10:e61432. doi: 10.7554/eLife.61432. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33570491 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic hedgehog signaling in astrocytes.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Feb;78(4):1393-1403. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03668-8. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33079226 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Voutsinos-Porche B., Bonvento G., Tanaka K., Steiner P., Welker E., Chatton J.-Y., Magistretti P. J., and Pellerin L. (2003) Glial glutamate transporters mediate a functional metabolic crosstalk between neurons and astrocytes in the mouse developing cortex. Neuron 37, 275–286 10.1016/S0896-6273(02)01170-4 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

