Metagenomes from Coastal Marine Sediments Give Insights into the Ecological Role and Cellular Features of Loki- and Thorarchaeota
- PMID: 31506313
- PMCID: PMC6737245
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.02039-19
Metagenomes from Coastal Marine Sediments Give Insights into the Ecological Role and Cellular Features of Loki- and Thorarchaeota
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Manoharan et al., "Metagenomes from Coastal Marine Sediments Give Insights into the Ecological Role and Cellular Features of Loki- and Thorarchaeota".mBio. 2019 Oct 29;10(5):e02509-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02509-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31662461 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
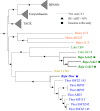
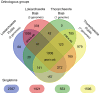
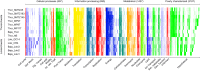
The genomes of Asgard Archaea, a novel archaeal proposed superphylum, share an enriched repertoire of eukaryotic signature genes and thus promise to provide insights into early eukaryote evolution. However, the distribution, metabolisms, cellular structures, and ecology of the members within this superphylum are not well understood. Here we provide a meta-analysis of the environmental distribution of the Asgard archaea, based on available 16S rRNA gene sequences. Metagenome sequencing of samples from a salt-crusted lagoon on the Baja California Peninsula of Mexico allowed the assembly of a new Thorarchaeota and three Lokiarchaeota genomes. Comparative analyses of all known Lokiarchaeota and Thorarchaeota genomes revealed overlapping genome content, including central carbon metabolism. Members of both groups contained putative reductive dehalogenase genes, suggesting that these organisms might be able to metabolize halogenated organic compounds. Unlike the first report on Lokiarchaeota, we identified genes encoding glycerol-1-phosphate dehydrogenase in all Loki- and Thorarchaeota genomes, suggesting that these organisms are able to synthesize bona fide archaeal lipids with their characteristic glycerol stereochemistry.IMPORTANCE Microorganisms of the superphylum Asgard Archaea are considered to be the closest living prokaryotic relatives of eukaryotes (including plants and animals) and thus promise to give insights into the early evolution of more complex life forms. However, very little is known about their biology as none of the organisms has yet been cultivated in the laboratory. Here we report on the ecological distribution of Asgard Archaea and on four newly sequenced genomes of the Lokiarchaeota and Thorarchaeota lineages that give insight into possible metabolic features that might eventually help to identify these enigmatic groups of archaea in the environment and to culture them.
Keywords: Archaea; Lokiarchaeota; Thorarchaeota; ether lipids; eukaryotic evolution; reductive dehalogenase.
Copyright © 2019 Manoharan et al.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative genomic inference suggests mixotrophic lifestyle for Thorarchaeota.ISME J. 2018 Apr;12(4):1021-1031. doi: 10.1038/s41396-018-0060-x. Epub 2018 Feb 14. ISME J. 2018. PMID: 29445130 Free PMC article.
-
Ecological features and global distribution of Asgard archaea.Sci Total Environ. 2021 Mar 1;758:143581. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143581. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 33223169
-
Proposal of the reverse flow model for the origin of the eukaryotic cell based on comparative analyses of Asgard archaeal metabolism.Nat Microbiol. 2019 Jul;4(7):1138-1148. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0406-9. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Nat Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30936488
-
Asgard archaea in saline environments.Extremophiles. 2022 Jun 28;26(2):21. doi: 10.1007/s00792-022-01266-z. Extremophiles. 2022. PMID: 35761090 Review.
-
Asgard archaea: Diversity, function, and evolutionary implications in a range of microbiomes.AIMS Microbiol. 2019 Jan 30;5(1):48-61. doi: 10.3934/microbiol.2019.1.48. eCollection 2019. AIMS Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31384702 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expanded Archaeal Genomes Shed New Light on the Evolution of Isoprenoid Biosynthesis.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 30;12(4):707. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040707. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38674651 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative population genomic analyses of transporters within the Asgard archaeal superphylum.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 26;16(3):e0247806. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247806. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33770091 Free PMC article.
-
Unique mobile elements and scalable gene flow at the prokaryote-eukaryote boundary revealed by circularized Asgard archaea genomes.Nat Microbiol. 2022 Feb;7(2):200-212. doi: 10.1038/s41564-021-01039-y. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Nat Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35027677 Free PMC article.
-
Helarchaeota and co-occurring sulfate-reducing bacteria in subseafloor sediments from the Costa Rica Margin.ISME Commun. 2021 Jun 17;1(1):25. doi: 10.1038/s43705-021-00027-x. ISME Commun. 2021. PMID: 36737514 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving Perspective on the Origin and Diversification of Cellular Life and the Virosphere.Genome Biol Evol. 2022 May 31;14(6):evac034. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evac034. Genome Biol Evol. 2022. PMID: 35218347 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zaremba-Niedzwiedzka K, Caceres EF, Saw JH, Bäckström D, Juzokaite L, Vancaester E, Seitz KW, Anantharaman K, Starnawski P, Kjeldsen KU, Stott MB, Nunoura T, Banfield JF, Schramm A, Baker BJ, Spang A, Ettema T. 2017. Asgard archaea illuminate the origin of eukaryotic cellular complexity. Nature 541:353–358. doi:10.1038/nature21031. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

