Anti-TNF therapy in IBD exerts its therapeutic effect through macrophage IL-10 signalling
- PMID: 31506328
- PMCID: PMC7282553
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318264
Anti-TNF therapy in IBD exerts its therapeutic effect through macrophage IL-10 signalling
Abstract
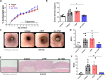
Objective: Macrophage interleukin (IL)-10 signalling plays a critical role in the maintenance of a regulatory phenotype that prevents the development of IBD. We have previously found that anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF) monoclonal antibodies act through Fcγ-receptor (FcγR) signalling to promote repolarisation of proinflammatory intestinal macrophages to a CD206+ regulatory phenotype. The role of IL-10 in anti-TNF-induced macrophage repolarisation has not been examined.
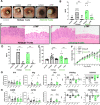
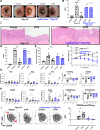
Design: We used human peripheral blood monocytes and mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages to study IL-10 production and CD206+ regulatory macrophage differentiation. To determine whether the efficacy of anti-TNF was dependent on IL-10 signalling in vivo and in which cell type, we used the CD4+CD45Rbhigh T-cell transfer model in combination with several genetic mouse models.
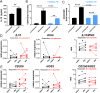
Results: Anti-TNF therapy increased macrophage IL-10 production in an FcγR-dependent manner, which caused differentiation of macrophages to a more regulatory CD206+ phenotype in vitro. Pharmacological blockade of IL-10 signalling prevented the induction of these CD206+ regulatory macrophages and diminished the therapeutic efficacy of anti-TNF therapy in the CD4+CD45Rbhigh T-cell transfer model of IBD. Using cell type-specific IL-10 receptor mutant mice, we found that IL-10 signalling in macrophages but not T cells was critical for the induction of CD206+ regulatory macrophages and therapeutic response to anti-TNF.
Conclusion: The therapeutic efficacy of anti-TNF in resolving intestinal inflammation is critically dependent on IL-10 signalling in macrophages.
Keywords: IBD basic research; TNF; antibody targeted therapy; infliximab; interleukins.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: AKG and ABvtW are employees of Janssen Vaccines and Prevention B.V. GRvdB is currently an employee of Roche. CYP received research support from Takeda, speaker’s fees from Takeda, Abbvie and Dr. Falk Pharma, and consultancy fee from Takeda outside this work. Other authors declare no conflict of interest related to this work.
Figures



References
-
- Fleischmann R, Vencovsky J, van Vollenhoven RF, et al. . Efficacy and safety of certolizumab pegol monotherapy every 4 weeks in patients with rheumatoid arthritis failing previous disease-modifying antirheumatic therapy: the FAST4WARD study. Ann Rheum Dis 2009;68:805–11. 10.1136/ard.2008.099291 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
