ePath: an online database towards comprehensive essential gene annotation for prokaryotes
- PMID: 31506471
- PMCID: PMC6737131
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-49098-w
ePath: an online database towards comprehensive essential gene annotation for prokaryotes
Abstract
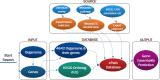
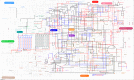
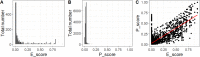
Experimental techniques for identification of essential genes (EGs) in prokaryotes are usually expensive, time-consuming and sometimes unrealistic. Emerging in silico methods provide alternative methods for EG prediction, but often possess limitations including heavy computational requirements and lack of biological explanation. Here we propose a new computational algorithm for EG prediction in prokaryotes with an online database (ePath) for quick access to the EG prediction results of over 4,000 prokaryotes ( https://www.pubapps.vcu.edu/epath/ ). In ePath, gene essentiality is linked to biological functions annotated by KEGG Ortholog (KO). Two new scoring systems, namely, E_score and P_score, are proposed for each KO as the EG evaluation criteria. E_score represents appearance and essentiality of a given KO in existing experimental results of gene essentiality, while P_score denotes gene essentiality based on the principle that a gene is essential if it plays a role in genetic information processing, cell envelope maintenance or energy production. The new EG prediction algorithm shows prediction accuracy ranging from 75% to 91% based on validation from five new experimental studies on EG identification. Our overall goal with ePath is to provide a comprehensive and reliable reference for gene essentiality annotation, facilitating the study of those prokaryotes without experimentally derived gene essentiality information.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 DE018138/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE023078/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01DE018138/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR)/International
- R01DE023078/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

