Biological surface properties in extracellular vesicles and their effect on cargo proteins
- PMID: 31506490
- PMCID: PMC6736982
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-47598-3
Biological surface properties in extracellular vesicles and their effect on cargo proteins
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Biological surface properties in extracellular vesicles and their effect on cargo proteins.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 5;9(1):18715. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54948-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31804587 Free PMC article.
Abstract
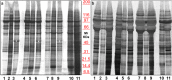
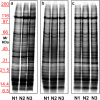
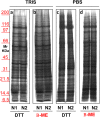
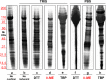
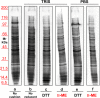
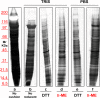
Ultracentrifugationon sucrose density gradientappears to be the best purification protocol for extracellular vesicle (EVs) purification. After this step, to reduce disulfide bridges linking exogenous proteins to the vesicles, the collected samples are routinely washed and treated with dithiothreitol (DTT). Such incubations are performed at temperatures ranging from room temperature up to 95 °C, with either Tris or PBS as buffers. We re-investigated these steps on both exosomes and microvesicles purified from blood (serum) and urine by electrophoretic separation, silver staining and western blots analysis. Data confirm that an extra centrifugation on a sucrose cushion can effectively eliminate contaminants. Tris buffer (50 Mm) and β-mercaptoethanol as a reducing agent at room temperature dramatically improved either sample cleaning. By contrast, especially for exosomes PBS buffer and DTT, above 37 °C, caused massive protein aggregations, yielding blurred SDS-PAGE gels in both samples. Immuno-blot analyses demonstrated that in PBS-DTT contamination with albumin (in serum) or with uromodulin (in urine) occurs. DTT, likely due to its two-SH groups, might form scrambled SS-bonds promoting EVs interaction with environmental macromolecules via disulphide bridges. Therefore, to obtain maximum vesicle purity for biomarker investigations and to maximize both presence of EVs proteins and their accessibility, use of DTT is not recommended.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

