Predictors for Pulmonary Tuberculosis Treatment Outcome in Denmark 2009-2014
- PMID: 31506499
- PMCID: PMC6736960
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-49439-9
Predictors for Pulmonary Tuberculosis Treatment Outcome in Denmark 2009-2014
Abstract
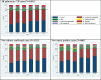
Monitoring of tuberculosis (TB) treatment outcome is essential to ensure an effective TB control program. In this nationwide retrospective cohort study from Denmark we present TB treatment outcome rates and risk factors associated with an unfavourable outcome. All patients notified with pulmonary TB from 2009 through 2014 were included. Logistic regression analyses were used to identify risk factors for unfavourable outcome. In total, 1681 pulmonary TB cases were included. TB treatment success rates increased during the study period. In 2014, the treatment success rate reached 85% for new culture positive cases whereas 7% cases interrupted treatment. The mortality decreased during the study period from 12.3% to 4.1%. Several risk factors associated with unfavourable outcome were identified in a multivariable model: male (OR: 2.56), Greenlandic origin (OR: 1.80), abuse of alcohol (OR: 2.90), history of mental disorder (OR: 2.46), and anaemia at time of treatment initiation (OR: 1.92). In a TB low incidence setting such as the Danish, it is important to maintain focus on preventing an unfavourable TB outcome. Patient management and treatment can be optimized by taking into consideration risk factors such as those identified in the present study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Cegielski J. Peter, Dalton Tracy, Yagui Martin, Wattanaamornkiet Wanpen, Volchenkov Grigory V., Via Laura E., Van Der Walt Martie, Tupasi Thelma, Smith Sarah E., Odendaal Ronel, Leimane Vaira, Kvasnovsky Charlotte, Kuznetsova Tatiana, Kurbatova Ekaterina, Kummik Tiina, Kuksa Liga, Kliiman Kai, Kiryanova Elena V., Kim HeeJin, Kim Chang-ki, Kazennyy Boris Y., Jou Ruwen, Huang Wei-Lun, Ershova Julia, Erokhin Vladislav V., Diem Lois, Contreras Carmen, Cho Sang Nae, Chernousova Larisa N., Chen Michael P., Caoili Janice Campos, Bayona Jaime, Akksilp Somsak, Calahuanca Gloria Yale, Wolfgang Melanie, Viiklepp Piret, Vasilieva Irina A., Taylor Allison, Tan Kathrine, Suarez Carmen, Sture Ingrida, Somova Tatiana, Smirnova Tatyana G., Sigman Erika, Skenders Girts, Sitti Wanlaya, Shamputa Isdore C., Riekstina Vija, Pua Kristine Rose, Therese M., Perez C., Park Seungkyu, Norvaisha Inga, Nemtsova Evgenia S., Min Seonyeong, Metchock Beverly, Levina Klavdia, Lei Yung-Chao, Lee Jongseok, Larionova Elena E., Lancaster Joey, Jeon Doosoo, Jave Oswaldo, Khorosheva Tatiana, Hwang Soo Hee, Huang Angela Song-En, Gler M. Tarcela, Dravniece Gunta, Eum Seokyong, Demikhova Olga V., Degtyareva Irina, Danilovits Manfred, Cirula Anda, Cho Eunjin, Cai Ying, Brand Jeanette, Bonilla Cesar, Barry Clifton E., Asencios Luis, Andreevskaya Sofia N., Akksilp Rattanawadee. Extensive Drug Resistance Acquired During Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2014;59(8):1049–1063. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu572. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Statens Serum Institut. Tuberkulosebehandling 2008–2010, www.ssi.dk/aktuelt/nyhedsbreve/epi-nyt/2013/Uge27-2013. (Date last updated 2013. Date last accesed: Jan 1 2019).
-
- WHO Regional Office for Europe/European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Tuberculosis surveillance and monitoring in Europe 2019–2017 data. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe; (2019).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

