A new recombinant MS-superoxide dismutase alleviates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice
- PMID: 31506573
- PMCID: PMC7468365
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-019-0295-8
A new recombinant MS-superoxide dismutase alleviates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice
Abstract
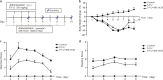
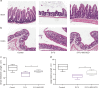
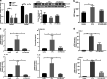
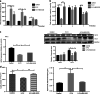
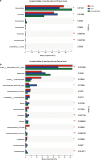
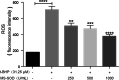
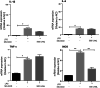
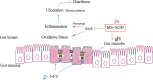
Intestinal mucositis is a common side effect of anticancer regimens that exerts a negative impact on chemotherapy. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) is a potential therapy for mucositis but efficient product is not available because the enzyme is degraded following oral administration or induces an immune reaction after intravascular infusion. Multi-modified Stable Anti-Oxidant Enzymes® (MS-AOE®) is a new recombinant SOD with better resistance to pepsin and trypsin. We referred it as MS-SOD to distinguish from other SODs. In this study we investigated its potential to alleviate 5-FU-induced intestinal injury and the mechanisms. An intestinal mucositis model was established in C57/BL6 mice by 5-day administration of 5-FU (50 mg/kg every day, ip). MS-SOD (800 IU/10 g, ig) was given once daily for 9 days. 5-FU caused severe mucositis with intestinal morphological damage, bodyweight loss and diarrhea; MS-SOD significantly decreased the severity. 5-FU markedly increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammatory cytokines in the intestine which were ameliorated by MS-SOD. Furthermore, MS-SOD modified intestinal microbes, particularly reduced Verrucomicrobia, compared with the 5-FU group. In Caco2 cells, MS-SOD (250-1000 U/mL) dose-dependently decreased tBHP-induced ROS generation. In RAW264.7 cells, MS-SOD (500 U/mL) had no effect on LPS-induced inflammatory cytokines, but inhibited iNOS expression. These results demonstrate that MS-SOD can scavenge ROS at the initial stage of injury, thus play an indirect role in anti-inflammatory and barrier protein protection. In conclusion, MS-SOD attenuates 5-FU-induced intestinal mucositis by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation, and influencing microbes. MS-SOD may exert beneficial effect in prevention of intestinal mucositis during chemotherapy in clinic.
Keywords: 5-fluorouracil; chemotherapy; cytokines; diarrhea; intestinal microbes; intestinal mucositis; manganese superoxide dismutase; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenthal DI, Mendoza TR, Fuller CD, Hutcheson KA, Wang XS, Hanna EY, et al. Patterns of symptom burden during radiotherapy or concurrent chemoradiotherapy for head and neck cancer: a prospective analysis using the university of Texas MD anderson cancer center symptom inventory‐head and neck module. Cancer. 2014;120:1975–84. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28672. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iacovelli R, Pietrantonio F, Palazzo A, Maggi C, Ricchini F, de Braud F, et al. Incidence and relative risk of grade 3 and 4 diarrhoea in patients treated with capecitabine or 5-fluorouracil: a meta-analysis of published trials. Br J Clin Pharm. 2014;78:1228–37. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12449. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Simone NL, Menard C, Soule BP, Albert PS, Guion P, Smith S, et al. Intrarectal amifostine during external beam radiation therapy for prostate cancer produces significant improvements in quality of life measured by epic score. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:90–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.05.057. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

