Aberrant reward dynamics in trait anticipatory anhedonia
- PMID: 31506689
- PMCID: PMC6847339
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nsz062
Aberrant reward dynamics in trait anticipatory anhedonia
Abstract
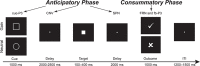
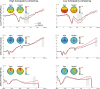
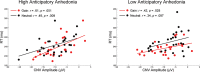
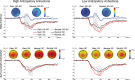
As a cardinal feature of several psychiatric disorders, anhedonia includes a consummatory component (deficits in hedonic response to rewards) and an anticipatory component (a reduced motivation to pursue them). Although being conceptualized as impairments of reward system, the neural characterization of reward processing in anhedonia is hampered by the enormous heterogeneity in the reward phase ('wanting' vs 'liking') and comorbidity (inherent to disease states). The current event-related potential (ERP) study examined the reward dynamics of anticipatory anhedonia in a non-clinical sample. Anticipatory and consummatory ERP components were assessed with a monetary incentive delay task in a high anticipatory anhedonia (HAA) group and a low anticipatory anhedonia (LAA) group. HAA vs LAA group showed a diminished reward-related speeding during behavioral performance and reported overall reduced positive affect during anticipation and receipt of outcomes. Importantly, neural dynamics underlying reward processing were negatively associated with anticipatory anhedonia across the anticipatory phase indexed by the contingent negative variation and the consummatory phase indexed by the feedback P3. Our results suggest that anticipatory anhedonia in non-clinical individuals is linked to a poor modulation during both anticipatory and consummatory phases of reward processing.
Keywords: anticipatory anhedonia; event-related potentials; reward dynamics.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aberrant reward dynamics in depression with anticipatory anhedonia.Clin Neurophysiol. 2023 Oct;154:34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2023.05.014. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Clin Neurophysiol. 2023. PMID: 37541075
-
Teasing apart the anticipatory and consummatory processing of monetary incentives: An event-related potential study of reward dynamics.Psychophysiology. 2015 Nov;52(11):1470-82. doi: 10.1111/psyp.12504. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Psychophysiology. 2015. PMID: 26223291
-
Differential effects of acute stress on anticipatory and consummatory phases of reward processing.Neuroscience. 2014 Apr 25;266:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.01.058. Epub 2014 Feb 7. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24508744 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine dysregulation hypothesis: the common basis for motivational anhedonia in major depressive disorder and schizophrenia?Rev Neurosci. 2018 Sep 25;29(7):727-744. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2017-0091. Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29573379 Review.
-
[Anhedonia in depression].Encephale. 2013 Sep;39(4):296-305. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2013.07.001. Epub 2013 Aug 12. Encephale. 2013. PMID: 23937895 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Social Incentives Anticipation and Consummation: Investigating Neural Activity in Women Using Methamphetamine.Front Psychol. 2020 Jan 28;11:88. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00088. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32047469 Free PMC article.
-
Neural dynamics of monetary and social reward processing in social anhedonia.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2020 Nov 6;15(9):991-1003. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsaa128. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32945882 Free PMC article.
-
Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction Specifically Improves Social Anhedonia Among Adults with Chronic Stress.Affect Sci. 2021 Nov 9;3(1):145-159. doi: 10.1007/s42761-021-00085-3. eCollection 2022 Mar. Affect Sci. 2021. PMID: 36046096 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced neural responses to reward reflect anhedonia and inattention: an ERP study.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 19;12(1):17432. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21591-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36261598 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berridge K.C., Robinson T.E. (2003). Parsing reward. Trends in Neurosciences, 26(9), 507–13. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard J.J., Horan W.P., Brown S.A. (2001). Diagnostic differences in social anhedonia: a longitudinal study of schizophrenia and major depressive disorder. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 110(3), 363–71. - PubMed
-
- Broyd S.J., Richards H.J., Helps S.K., Chronaki G., Bamford S., Sonuga-Barke E.J. (2012). An electrophysiological monetary incentive delay (e-MID) task: a way to decompose the different components of neural response to positive and negative monetary reinforcement. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 209(1), 40–9. - PubMed
-
- Brunia C.H. (1988). Movement and stimulus preceding negativity. Biological Psychology, 26(1–3), 165–78. - PubMed
-
- Brunia C.H., Hackley S.A., van Boxtel G.J., Kotani Y., Ohgami Y. (2011). Waiting to perceive: reward or punishment? Clinical Neurophysiology, 122(5), 858–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

