A novel neural computational model of generalized periodic discharges in acute hepatic encephalopathy
- PMID: 31506807
- PMCID: PMC6881550
- DOI: 10.1007/s10827-019-00727-3
A novel neural computational model of generalized periodic discharges in acute hepatic encephalopathy
Abstract
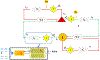
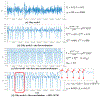
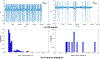
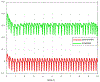
Acute hepatic encephalopathy (AHE) due to acute liver failure is a common form of delirium, a state of confusion, impaired attention, and decreased arousal. The electroencephalogram (EEG) in AHE often exhibits a striking abnormal pattern of brain activity, which epileptiform discharges repeat in a regular repeating pattern. This pattern is known as generalized periodic discharges, or triphasic-waves (TPWs). While much is known about the neurophysiological mechanisms underlying AHE, how these mechanisms relate to TPWs is poorly understood. In order to develop hypotheses how TPWs arise, our work builds a computational model of AHE (AHE-CM), based on three modifications of the well-studied Liley model which emulate mechanisms believed central to brain dysfunction in AHE: increased neuronal excitability, impaired synaptic transmission, and enhanced postsynaptic inhibition. To relate our AHE-CM to clinical EEG data from patients with AHE, we design a model parameter optimization method based on particle filtering (PF-POM). Based on results from 7 AHE patients, we find that the proposed AHE-CM not only performs well in reproducing important aspects of the EEG, namely the periodicity of triphasic waves (TPWs), but is also helpful in suggesting mechanisms underlying variation in EEG patterns seen in AHE. In particular, our model helps explain what conditions lead to increased frequency of TPWs. In this way, our model represents a starting point for exploring the underlying mechanisms of brain dynamics in delirium by relating microscopic mechanisms to EEG patterns.
Keywords: Acute hepatic encephalopathy (AHE); Electroencephalogram (EEG); Generalized periodic discharges; Liley model; Neural computational model; Particle filtering.
Figures

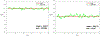

Similar articles
-
A Mean Field Model of Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018 Jul;2018:2366-2369. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2018.8512786. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018. PMID: 30440882 Free PMC article.
-
Do Triphasic Waves and Nonconvulsive Status Epilepticus Arise From Similar Mechanisms? A Computational Model.J Clin Neurophysiol. 2021 Sep 1;38(5):366-375. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0000000000000719. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 34155185 Free PMC article.
-
Cefepime-induced encephalopathy: Neural mass modeling of triphasic wave-like generalized periodic discharges with a high negative component (Tri-HNC).Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019 Jan;73(1):34-42. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12795. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30375126 Free PMC article.
-
Periodic EEG patterns: importance of their recognition and clinical significance.Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2012 Feb;70(2):145-51. doi: 10.1590/s0004-282x2012000200014. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2012. PMID: 22311221 Review.
-
Neural network modeling of EEG patterns in encephalopathy.J Clin Neurophysiol. 2013 Oct;30(5):545-52. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e3182a73e16. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 24084188 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive investigation of intracortical and corticothalamic models of the alpha rhythm.PLoS Comput Biol. 2025 Apr 10;21(4):e1012926. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012926. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2025. PMID: 40209165 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence, associated factors, and outcomes of delirium in critically ill children in china: a prospective cohort study.BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Dec 11;23(1):925. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-05406-3. BMC Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 38082396 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying EEG power changes during wakefulness in insomnia patients: a model-driven study.Cogn Neurodyn. 2025 Dec;19(1):17. doi: 10.1007/s11571-024-10207-9. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Cogn Neurodyn. 2025. PMID: 39801916
-
Aperiodic stochastic resonance in neural information processing with Gaussian colored noise.Cogn Neurodyn. 2021 Jun;15(3):517-532. doi: 10.1007/s11571-020-09632-3. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Cogn Neurodyn. 2021. PMID: 34040675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amodio P, Del Piccolo F, Pettenò E, Mapelli D, Angeli P, Iemmolo R, Muraca M, Musto C, Gerunda G, Rizzo C, et al., Journal of hepatology 35(1), 37 (2001) - PubMed
-
- D’amico G, Morabito A, Pagliaro L, Marubini E, et al., Digestive diseases and sciences 31(5), 468 (1986) - PubMed
-
- Wijdicks EF, New England Journal of Medicine 375(17), 1660 (2016) - PubMed
-
- Hirsch L, LaRoche S, Gaspard N, Gerard E, Svoronos A, Herman S, Mani R, Arif H, Jette N, Minazad Y, et al., Journal of clinical neurophysiology 30(1), 1 (2013) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

