Fast-food restaurant, unhealthy eating, and childhood obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31507064
- PMCID: PMC7988557
- DOI: 10.1111/obr.12944
Fast-food restaurant, unhealthy eating, and childhood obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Excessive access to fast-food restaurants (FFRs) in the neighbourhood is thought to be a risk factor for childhood obesity by discouraging healthful dietary behaviours while encouraging the exposure to unhealthful food venues and hence the compensatory intake of unhealthy food option. A literature search was conducted in the PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase for articles published until 1 January 2019 that analysed the association between access to FFRs and weight-related behaviours and outcomes among children aged younger than 18. Sixteen cohort studies and 71 cross-sectional studies conducted in 14 countries were identified. While higher FFR access was not associated with weight-related behaviours (eg, dietary quality score and frequency of food consumption) in most studies, it was commonly associated with more fast-food consumption. Despite that, insignificant results were observed for all meta-analyses conducted by different measures of FFR access in the neighbourhood and weight-related outcomes, although 17 of 39 studies reported positive associations when using overweight/obesity as the outcome. This systematic review and meta-analysis revealed a rather mixed relationship between FFR access and weight-related behaviours/outcomes among children and adolescents.
Keywords: dietary behaviour; fast food; food environment; obesity.
© 2019 The Authors. Obesity Reviews published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of World Obesity Federation.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest was declared.
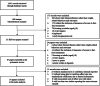
Figures


References
-
- Curran PJ. The semivariogram in remote sensing: an introduction. Remote Sens Environ. 1988;24:15.
-
- Kelsey MM, Zaepfel A, Bjornstad P, Nadeau KJ. Age‐related consequences of childhood obesity. Gerontology. 2014;60(3):222‐228. - PubMed
-
- Report of the commission on ending childhood obesity. World Health Organization ;2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

