High-Fat Diet Increases Amylin Accumulation in the Hippocampus and Accelerates Brain Aging in hIAPP Transgenic Mice
- PMID: 31507407
- PMCID: PMC6718729
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00225
High-Fat Diet Increases Amylin Accumulation in the Hippocampus and Accelerates Brain Aging in hIAPP Transgenic Mice
Abstract
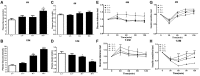
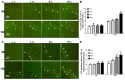
The accumulation of human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP) in pancreatic islets under induction by a high-fat diet plays a critical role in the development of type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). T2DM is a risk factor of late-onset Alzheimer's disease (AD). Nevertheless, whether hIAPP in combination with hyperlipidemia may lead to AD-like pathological changes in the brain remains unclear. hIAPP transgenic mice were fed with a high-fat diet for 6 or 12 months to establish the T2DM model. The accumulation of amylin, the numbers of Fluoro-Jade C (FJC)-positive and β-gal positive cells, and the deposition level of Aβ42 in the hippocampi of the transgenic mice were detected by using brain sections. Cytoplasmic and membrane proteins were extracted from the hippocampi of the transgenic mice, and the ratio of membrane GLUT4 expression to cytoplasmic GLUT4 expression was measured through Western blot analysis. Changes in the cognitive functions of hIAPP transgenic mice after 12 months of feeding with a high-fat diet were evaluated. hIAPP transgenic mice fed with a high-fat diet for 6 or 12 months showed elevated blood glucose levels and insulin resistance; increased amylin accumulation, number of FJC-positive and β-gal positive cells, and Aβ42 deposition in the hippocampi; and reduced membrane GLUT4 expression levels. hIAPP transgenic mice fed with a high-fat diet for 12 months showed reductions in social cognitive ability and passive learning ability. A high-fat diet increased amylin accumulation in the hippocampi of hIAPP transgenic mice, which presented AD-like pathology and behavior characterized by neural degeneration, brain aging, Aβ42 deposition, and impaired glucose utilization and cognition.
Keywords: brain aging; cognition; high-fat diet; hippocampus; human islet amyloid polypeptide.
Figures





Similar articles
-
beta-cell glucokinase deficiency and hyperglycemia are associated with reduced islet amyloid deposition in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes.Diabetes. 2000 Dec;49(12):2056-62. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.49.12.2056. Diabetes. 2000. PMID: 11118007
-
Interaction of human IAPP and Aβ1-42 aggravated the AD-related pathology and impaired the cognition in mice.Exp Neurol. 2020 Dec;334:113490. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113490. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33007295
-
Increased dietary fat promotes islet amyloid formation and beta-cell secretory dysfunction in a transgenic mouse model of islet amyloid.Diabetes. 2003 Feb;52(2):372-9. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.52.2.372. Diabetes. 2003. PMID: 12540610
-
The potential role of human islet amyloid polypeptide in type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer's diseases.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023 May 13;15(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13098-023-01082-1. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023. PMID: 37173803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human IAPP amyloidogenic properties and pancreatic β-cell death.Cell Calcium. 2014 Nov;56(5):416-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2014.08.011. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Cell Calcium. 2014. PMID: 25224501 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipids determine the toxicity of human islet polypeptide aggregates in vivo.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jan;301(1):108029. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.108029. Epub 2024 Nov 29. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39615682 Free PMC article.
-
A pancreatic player in dementia: pathological role for islet amyloid polypeptide accumulation in the brain.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Oct;18(10):2141-2146. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.369095. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 37056121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-fibril form but not fibril form of human islet amyloid polypeptide 8-20 changes brain functions in mice.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 5;19(1):e0296750. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296750. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38181010 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Animal Models for Studying Bone Health in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) and Obesity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 29;25(17):9399. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179399. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ApoE isoform-dependent effects of xanthohumol on high fat diet-induced cognitive impairments and hippocampal metabolic pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 3;13:954980. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.954980. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36278228 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreetto E., Yan L. M., Tatarek-Nossol M., Velkova A., Frank R., Kapurniotu A. (2010). Identification of hot regions of the Aβ-IAPP interaction interface as high-affinity binding sites in both cross- and self-association. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed Engl. 49, 3081–3085. 10.1002/anie.200904902 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

