IK1 Channel Agonist Zacopride Alleviates Cardiac Hypertrophy and Failure via Alterations in Calcium Dyshomeostasis and Electrical Remodeling in Rats
- PMID: 31507422
- PMCID: PMC6718093
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00929
IK1 Channel Agonist Zacopride Alleviates Cardiac Hypertrophy and Failure via Alterations in Calcium Dyshomeostasis and Electrical Remodeling in Rats
Abstract
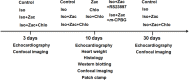
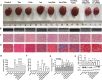
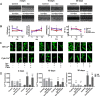
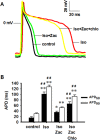
Intracellular Ca2+ overload, prolongation of the action potential duration (APD), and downregulation of inward rectifier potassium (IK1) channel are hallmarks of electrical remodeling in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure (HF). We hypothesized that enhancement of IK1 currents is a compensation for IK1 deficit and a novel modulation for cardiac Ca2+ homeostasis and pathological remodeling. In adult Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats in vivo, cardiac hypertrophy was induced by isoproterenol (Iso) injection (i.p., 3 mg/kg/d) for 3, 10, and 30 days. Neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (NRVMs) were isolated from 1 to 3 days SD rat pups and treated with 1 μmol/L Iso for 24 h in vitro. The effects of zacopride, a selective IK1/Kir2.1 channel agonist, on cardiac remodeling/hypertrophy were observed in the settings of 15 μg/kg in vivo and 1 μmol/L in vitro. After exposing to Iso for 3 days and 10 days, rat hearts showed distinct concentric hypertrophy and fibrosis and enhanced pumping function (P < 0.01 or P < 0.05), then progressed to dilatation and dysfunction post 30 days. Compared with the age-matched control, cardiomyocytes exhibited higher cytosolic Ca2+ (P < 0.01 or P < 0.05) and lower SR Ca2+ content (P < 0.01 or P < 0.05) all through 3, 10, and 30 days of Iso infusion. The expressions of Kir2.1 and SERCA2 were downregulated, while p-CaMKII, p-RyR2, and cleaved caspase-3 were upregulated. Iso-induced electrophysiological abnormalities were also manifested with resting potential (RP) depolarization (P < 0.01), APD prolongation (P < 0.01) in adult cardiomyocytes, and calcium overload in cultured NRVMs (P < 0.01). Zacopride treatment effectively retarded myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis, preserved the expression of Kir2.1 and some key players in Ca2+ homeostasis, normalized the RP (P < 0.05), and abbreviated APD (P < 0.01), thus lowered cytosolic [Ca2 +]i (P < 0.01 or P < 0.05). IK1channel blocker BaCl2 or chloroquine largely reversed the cardioprotection of zacopride. We conclude that cardiac electrical remodeling is concurrent with structural remodeling. By enhancing cardiac IK1, zacopride prevents Iso-induced electrical remodeling around intracellular Ca2+ overload, thereby attenuates cardiac structural disorder and dysfunction. Early electrical interventions may provide protection on cardiac remodeling.
Keywords: calcium overload; cardiac remodeling; inward rectifier potassium channel; isoproterenol; zacopride.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cardioprotection of an IK1 channel agonist on L-thyroxine induced rat ventricular remodeling.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Aug 15;13(8):8683-8696. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34539987 Free PMC article.
-
The IK1/Kir2.1 channel agonist zacopride prevents and cures acute ischemic arrhythmias in the rat.PLoS One. 2017 May 18;12(5):e0177600. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177600. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28542320 Free PMC article.
-
Tetramisole is a new IK1 channel agonist and exerts IK1 -dependent cardioprotective effects in rats.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2022 Aug;10(4):e00992. doi: 10.1002/prp2.992. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2022. PMID: 35880674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Agonist of Inward Rectifier Potassium Channel (IK1) Attenuates Rat Reperfusion Arrhythmias Linked to CaMKII Signaling.Int Heart J. 2021;62(6):1348-1357. doi: 10.1536/ihj.21-379. Int Heart J. 2021. PMID: 34853227
-
Caveolin-3 Microdomain: Arrhythmia Implications for Potassium Inward Rectifier and Cardiac Sodium Channel.Front Physiol. 2018 Nov 9;9:1548. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01548. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30473666 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of injection of different doses of isoproterenol on the hearts of mice.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022 Sep 12;22(1):409. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02852-x. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022. PMID: 36096747 Free PMC article.
-
Towards the Development of AgoKirs: New Pharmacological Activators to Study Kir2.x Channel and Target Cardiac Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 11;21(16):5746. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165746. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32796537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of Kir2.1 improves myocardial fibrosis by inhibiting Ca 2+ overload and the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023 May 15;55(5):749-757. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2023083. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023. PMID: 37184279 Free PMC article.
-
Barium Chloride-Induced Cardiac Arrhythmia Mouse Model Exerts an Experimental Arrhythmia for Pharmacological Investigations.Life (Basel). 2024 Aug 22;14(8):1047. doi: 10.3390/life14081047. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202788 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory mechanism of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in the occurrence and development of ventricular arrhythmia (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jun;21(6):656. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10088. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33968186 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aronow W. S., Epstein S., Koenigsberg M., Schwartz K. S. (1988). Usefulness of echocardiographic left ventricular hypertrophy, ventricular tachycardia and complex ventricular arrhythmias in predicting ventricular fibrillation or sudden cardiac death in elderly patients. Am. J. Cardiol. 62, 1124–1125. 10.1016/0002-9149(88)90562-0 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

