MRI Atlas of the Human Deep Brain
- PMID: 31507507
- PMCID: PMC6718608
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00851
MRI Atlas of the Human Deep Brain
Abstract
Mastering detailed anatomy of the human deep brain in clinical neurosciences is challenging. Although numerous pioneering works have gathered a large dataset of structural and topographic information, it is still difficult to transfer this knowledge into practice, even with advanced magnetic resonance imaging techniques. Thus, classical histological atlases continue to be used to identify structures for stereotactic targeting in functional neurosurgery. Physicians mainly use these atlases as a template co-registered with the patient's brain. However, it is possible to directly identify stereotactic targets on MRI scans, enabling personalized targeting. In order to help clinicians directly identify deep brain structures relevant to present and future medical applications, we built a volumetric MRI atlas of the deep brain (MDBA) on a large scale (infra millimetric). Twelve hypothalamic, 39 subthalamic, 36 telencephalic, and 32 thalamic structures were identified, contoured, and labeled. Nineteen coronal, 18 axial, and 15 sagittal MRI plates were created. Although primarily designed for direct labeling, the anatomic space was also subdivided in twelfths of AC-PC distance, leading to proportional scaling in the coronal, axial, and sagittal planes. This extensive work is now available to clinicians and neuroscientists, offering another representation of the human deep brain ([https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/] [hal-02116633]). The atlas may also be used by computer scientists who are interested in deciphering the topography of this complex region.
Keywords: MRI; atlas; deep brain; human; hypothalamus; stereotaxis; subthalamus; thalamus.
Figures

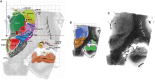

Similar articles
-
Reliability of atlas-derived coordinates in deep brain stimulation.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2005 Nov;147(11):1175-80; discussion 1180. doi: 10.1007/s00701-005-0606-3. Epub 2005 Aug 22. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2005. PMID: 16133776
-
Defining the anterior nucleus of the thalamus (ANT) as a deep brain stimulation target in refractory epilepsy: Delineation using 3 T MRI and intraoperative microelectrode recording.Neuroimage Clin. 2015 Mar 5;7:823-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.03.001. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2015. PMID: 26082891 Free PMC article.
-
Towards construction of an ideal stereotactic brain atlas.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2008 Jan;150(1):1-13; discussion 13-4. doi: 10.1007/s00701-007-1270-6. Epub 2007 Nov 21. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2008. PMID: 18030414
-
Toward defining deep brain stimulation targets in MNI space: A subcortical atlas based on multimodal MRI, histology and structural connectivity.Neuroimage. 2018 Apr 15;170:271-282. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.05.015. Epub 2017 May 20. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 28536045 Review.
-
A Brief History of Stereotactic Atlases: Their Evolution and Importance in Stereotactic Neurosurgery.Brain Sci. 2023 May 21;13(5):830. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13050830. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239302 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in severe Parkinson's disease: relationships between dual-contact topographic setting and 1-year worsening of speech and gait.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2023 Dec;165(12):3927-3941. doi: 10.1007/s00701-023-05843-9. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2023. PMID: 37889334
-
Anatomical brain structures normalization for deep brain stimulation in movement disorders.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;27:102271. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102271. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 32446242 Free PMC article.
-
Multiparametric MRI for Characterization of the Basal Ganglia and the Midbrain.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jun 21;15:661504. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.661504. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34234639 Free PMC article.
-
An MRI Deep Brain Adult Template With An Advanced Atlas-Based Tool For Diffusion Tensor Imaging Analysis.Sci Data. 2024 Nov 1;11(1):1189. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-04053-x. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 39487161 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of Human Brain Atlases in Terms of Content, Applications, Functionality, and Availability.Neuroinformatics. 2021 Jan;19(1):1-22. doi: 10.1007/s12021-020-09481-9. Neuroinformatics. 2021. PMID: 32728882 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schaltenbrand G, Wahren W. Atlas for Stereotaxy of the Human Brain. Stuttgart, NY: Thieme; (1977).
-
- Talairach J, David M, Tournoux P, Corredor H, Kvasina Atlas D'anatomie Stéréotaxique. Repérage Radiologique Indirect Des Noyaux Gris Centraux Des Régions Mésencéphalo-Sous-Optiques et Hypothalamiques de l'homme. Paris: Masson et Cie; (1957).
-
- Mai JK, Assheuer J, Paxinos G. Atlas of the Human Brain. London: Academic Press; (1977).
-
- Yelnik J, Bardinet E, Dormont D, Malandain G, Ourselin S, Tandé D, et al. . A three-dimensional, histological and deformable atlas of the human basal ganglia. I. atlas construction based on immunohistochemical and MRI data. NeuroImage. (2007) 34:618–638. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.09.026 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guiot G, Derome P, Trigo JC. Intention tremor: the best indication for stereotaxic surgery. La Presse Med. (1967) 75:2513–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

