Clinical Implications and Impact of Discovery of the Thyroid Hormone Receptor on Integrin αvβ3-A Review
- PMID: 31507530
- PMCID: PMC6716053
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00565
Clinical Implications and Impact of Discovery of the Thyroid Hormone Receptor on Integrin αvβ3-A Review
Abstract
Hypothyroidism has been reported to improve survival in cancer patients but only recently has the putative mechanism been identified as a receptor for thyroxine and tri-iodothyronine on integrin αvβ3. Recognition of divergence of action of the pro-oncogenic L-thyroxine (T4) from pro-metabolic 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine (T3) has enabled clinical implementation whereby exogenous T3 may replace exogenous (or endogenous) T4 to maintain clinical euthyroid hypothyroxinemia that results in significantly better survival in advanced cancer patients without the morbidity of clinical hypothyroidism.
Keywords: L-thyroxine; cancer; euthyroid hypothyroxinemia; hypothyroidism; integrin αvβ3; thyroid hormone receptor.
Figures


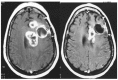
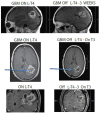

References
-
- Hercbergs A, Davis PJ, Lin H-Y, Keating KA, Mousa SA. Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy in Patients with Various Types of Cancer. in Hormone Therapy and Replacement in Cancer and Aging-related Diseases. InTechOpen (2019). Available online at: https://cdn.intechopen.com/pdfs/67201.pdf
-
- Hercbergs AA, Goyal LK, Suh JH, Lee S, Reddy CA, Cohen BH, et al. . Propylthiouracil-induced chemical hypothyroidism with high-dose tamoxifen prolongs survival in recurrent high grade glioma: a phase I/II study. Anticancer Res. (2003) 23:617–26. - PubMed
-
- Bergh JJ, Lin HY, Lansing L, Mohamed SN, Davis FB, Mousa S, et al. . Integrin αVβ3 contains a cell surface receptor site for thyroid hormone that is linked to activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and induction of angiogenesis. Endocrinology. (2005) 146:2864–71. 10.1210/en.2005-0102 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

