Post-transcriptional Regulation of HTLV Gene Expression: Rex to the Rescue
- PMID: 31507567
- PMCID: PMC6714889
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01958
Post-transcriptional Regulation of HTLV Gene Expression: Rex to the Rescue
Abstract
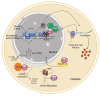
Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and other members of the Deltaretrovirus genus code for a regulatory protein named Rex that binds to the Rex-responsive element present on viral mRNAs. Rex rescues viral mRNAs from complete splicing or degradation and guides them to the cytoplasm for translation. The activity of Rex is essential for expression of viral transcripts coding for the virion components and thus represents a potential target for virus eradication. We present an overview of the functional properties of the HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 Rex proteins (Rex-1 and Rex-2), outline mechanisms controlling Rex function, and discuss similarities and differences in the sequences of Rex coded by HTLV-1, -2, -3, and -4 that may influence their molecular anatomy and functional properties.
Keywords: HTLV-1; HTLV-2; RNA export; Rex; splicing.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of Alternatively Spliced Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 mRNAs Is Influenced by Mitosis and by a Novel cis-Acting Regulatory Sequence.J Virol. 2015 Nov 18;90(3):1486-98. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02298-15. Print 2016 Feb 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26581997 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) type II Rex protein binds specifically to RNA sequences of the HTLV long terminal repeat but poorly to the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev-responsive element.J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2261-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.65.5.2261-2272.1991. J Virol. 1991. PMID: 2016758 Free PMC article.
-
Rex-dependent nucleolar accumulation of HTLV-I mRNAs.New Biol. 1991 Apr;3(4):389-97. New Biol. 1991. PMID: 2065024
-
The human T-cell leukemia virus Rex protein.Front Biosci. 2005 Jan 1;10:431-45. doi: 10.2741/1539. Print 2005 Jan 1. Front Biosci. 2005. PMID: 15574380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HTLV-1 Rex Tunes the Cellular Environment Favorable for Viral Replication.Viruses. 2016 Feb 24;8(3):58. doi: 10.3390/v8030058. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 26927155 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of Oncogenesis by HTLV-1 Tax.Pathogens. 2020 Jul 7;9(7):543. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9070543. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32645846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tuning Rex rules HTLV-1 pathogenesis.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 16;13:959962. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.959962. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36189216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinetics of HTLV-1 reactivation from latency quantified by single-molecule RNA FISH and stochastic modelling.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Nov 18;15(11):e1008164. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008164. eCollection 2019 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31738810 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-150 in HTLV-1 infection and T-cell transformation.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 16;13:974088. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.974088. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36072598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HTLV-1 Infection and Pathogenesis: New Insights from Cellular and Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 27;22(15):8001. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158001. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360767 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adachi Y., Copeland T. D., Takahashi C., Nosaka T., Ahmed A., Oroszlan S., et al. (1992). Phosphorylation of the Rex protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. J. Biol. Chem. 267 21977–21981. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

