Gga-miR-19b-3p Inhibits Newcastle Disease Virus Replication by Suppressing Inflammatory Response via Targeting RNF11 and ZMYND11
- PMID: 31507581
- PMCID: PMC6718473
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02006
Gga-miR-19b-3p Inhibits Newcastle Disease Virus Replication by Suppressing Inflammatory Response via Targeting RNF11 and ZMYND11
Abstract
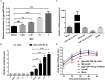
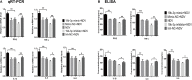
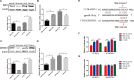
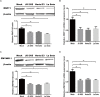
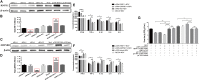
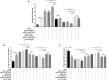
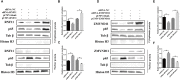
Newcastle disease (ND), an acute and highly contagious avian disease caused by virulent Newcastle disease virus (NDV), often results in severe economic losses worldwide every year. Although it is clear that microRNAs (miRNAs) are implicated in modulating innate immune response to invading microbial pathogens, their role in host defense against NDV infection remains largely unknown. Our prior study indicates that gga-miR-19b-3p is up-regulated in NDV-infected DF-1 cells (a chicken embryo fibroblast cell line) and functions to suppress NDV replication. Here we report that overexpression of gga-miR-19b-3p promoted the production of NDV-induced inflammatory cytokines and suppressed NDV replication, whereas inhibition of endogenous gga-miR-19b-3p expression had an opposite effect. Dual-luciferase and gene expression array analyses revealed that gga-miR-19b-3p directly targets the mRNAs of ring finger protein 11 (RNF11) and zinc-finger protein, MYND-type containing 11 (ZMYND11), two negative regulators of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling, in DF-1 cells. RNF11 and ZMYND11 silencing by small interfering RNA (siRNA) induced NF-κB activity and inflammatory cytokine production, and suppressed NDV replication; whereas ectopic expression of these two proteins exhibited an opposite effect. Our study provides evidence that gga-miR-19b-3p activates NF-κB signaling by targeting RNF11 and ZMYND11, and that enhanced inflammatory cytokine production is likely responsible for the suppression of NDV replication.
Keywords: DF-1 cells; NDV; NF-κB signaling; RNF11; ZMYND11; gga-miR-19b-3p; inflammatory cytokine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-19b-3p Modulates Japanese Encephalitis Virus-Mediated Inflammation via Targeting RNF11.J Virol. 2016 Apr 14;90(9):4780-4795. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02586-15. Print 2016 May. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26937036 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Expression Profiling in Newcastle Disease Virus-Infected DF-1 Cells by Deep Sequencing.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jul 23;10:1659. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01659. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31396181 Free PMC article.
-
Chicken gga-miR-19a Targets ZMYND11 and Plays an Important Role in Host Defense against Mycoplasma gallisepticum (HS Strain) Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Sep 14;6:102. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00102. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27683641 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
gga-miR-99a targets SMARCA5 to regulate Mycoplasma gallisepticum (HS strain) infection by depressing cell proliferation in chicken.Gene. 2017 Sep 5;627:239-247. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.06.039. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28652181 Review.
Cited by
-
Stress-Induced Immunosuppression Affects Immune Response to Newcastle Disease Virus Vaccine via Circulating miRNAs.Animals (Basel). 2022 Sep 12;12(18):2376. doi: 10.3390/ani12182376. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139236 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation by Non-Coding RNAs in the Avian Immune System.Life (Basel). 2020 Aug 12;10(8):148. doi: 10.3390/life10080148. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32806547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards Improved Use of Vaccination in the Control of Infectious Bronchitis and Newcastle Disease in Poultry: Understanding the Immunological Mechanisms.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Jan 4;9(1):20. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9010020. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33406695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Hub Genes With Differential Correlations in Sepsis.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 24;13:876514. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.876514. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35401666 Free PMC article.
-
Redox Homeostasis in Poultry: Regulatory Roles of NF-κB.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jan 28;10(2):186. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020186. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33525511 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartel D. P. (2004). MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116 281–297. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

