High Activation of γδ T Cells and the γδ2pos T-Cell Subset Is Associated With the Onset of Tuberculosis-Associated Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome, ANRS 12153 CAPRI NK
- PMID: 31507608
- PMCID: PMC6718564
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02018
High Activation of γδ T Cells and the γδ2pos T-Cell Subset Is Associated With the Onset of Tuberculosis-Associated Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome, ANRS 12153 CAPRI NK
Abstract
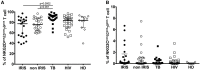
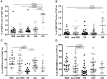
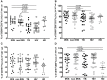
Background: Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 (HIV-1) and Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (Mtb) co-infected patients are commonly at risk of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) when initiating antiretroviral treatment (ART). Evidence indicates that innate immunity plays a role in TB-IRIS. Here, we evaluate the phenotype of Gamma-delta (γδ) T cells and invariant Natural Killer (iNK) T cells in tuberculosis-associated IRIS. Methods: Forty-eight HIV+/TB+ patients (21 IRIS) and three control groups: HIV-/TB- (HD, n = 11), HIV+/TB- (n = 26), and HIV-/TB+ (n = 22) were studied. Samples were taken at ART initiation (week 2 of anti-tuberculosis treatment) and at the diagnosis of IRIS for HIV+/TB+; before ART for HIV+/TB-, and at week 2 of anti-tuberculosis treatment for HIV-/TB+ patients. γδ T cells and Invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Results: Before ART, IRIS, and non-IRIS patients showed a similar proportion of γδpos T and iNKT cells. HLA-DR on γδpos T cells and δ2posγδpos T cells was significantly higher in TB-IRIS vs. non-IRIS patients and controls (p < 0.0001). NKG2D expression on γδpos T cells and the δ2posγδpos T cell subset was lower in HIV+/TB+ patients than controls. CD158a expression on γδpos T cells was higher in TB-IRIS than non-IRIS (p = 0.02), HIV+/TB-, and HIV-/TB- patients. Conclusion: The higher activation of γδposT cells and the γδ2posγδpos T cell subset suggests that γδ T cells may play a role in the pathogenesis of TB-IRIS.
Keywords: HIV; gamma delta T cells; immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome; invariant NKT cells; tuberculosis.
Figures


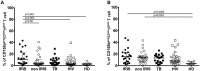
Similar articles
-
Changes in the NK Cell Repertoire Related to Initiation of TB Treatment and Onset of Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in TB/HIV Co-infected Patients in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil-ANRS 12274.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 13;10:1800. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01800. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31456797 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of T-Lymphocyte Activation Related to Paradoxical Tuberculosis-Associated Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in Persons With Advanced HIV.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 7;12:757843. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.757843. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34691079 Free PMC article.
-
Lower Pre-Treatment T Cell Activation in Early- and Late-Onset Tuberculosis-Associated Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0133924. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133924. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26208109 Free PMC article.
-
The immunopathogenesis of the HIV tuberculosis immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome.Eur J Immunol. 2013 Aug;43(8):1995-2002. doi: 10.1002/eji.201343632. Eur J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23928963 Review.
-
HIV-1 tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome.Semin Immunopathol. 2016 Mar;38(2):185-98. doi: 10.1007/s00281-015-0532-2. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Semin Immunopathol. 2016. PMID: 26423994 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unremitting pro-inflammatory T-cell phenotypes, and macrophage activity, following paediatric burn injury.Clin Transl Immunology. 2024 Mar 8;13(3):e1496. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1496. eCollection 2024. Clin Transl Immunology. 2024. PMID: 38463658 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the balance of Th17/Treg cells and oxidative stress markers in patients with HIV‑associated pulmonary tuberculosis who develop IRIS.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Apr 21;25(6):271. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.11970. eCollection 2023 Jun. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37206552 Free PMC article.
-
Tuberculosis IRIS: Pathogenesis, Presentation, and Management across the Spectrum of Disease.Life (Basel). 2020 Oct 29;10(11):262. doi: 10.3390/life10110262. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33138069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pooled evidence from preclinical and clinical studies for stem cell-based therapy in ARDS and COVID-19.Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 Jul;478(7):1487-1518. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04601-2. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36394787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updated outcomes and exploratory analysis of RENMIN-215: tislelizumab plus fruquintinib and fecal microbiota transplantation in refractory microsatellite stable metastatic colorectal cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Nov 15;14(11):5351-5364. doi: 10.62347/XKUJ3012. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39659943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laureillard D, Marcy O, Madec Y, Chea S, Chan S, Borand L, et al. . Paradoxical tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome after early initiation of antiretroviral therapy in a randomized clinical trial. AIDS. (2013) 27:2577–86. 10.1097/01.aids.0000432456.14099.c7 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

