Activation of Human NK Cells by Bordetella pertussis Requires Inflammasome Activation in Macrophages
- PMID: 31507615
- PMCID: PMC6718514
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02030
Activation of Human NK Cells by Bordetella pertussis Requires Inflammasome Activation in Macrophages
Abstract
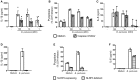
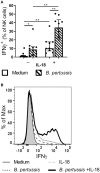
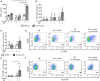
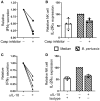
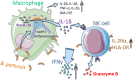
Pertussis is a highly contagious respiratory infection caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. Humans are the only known natural reservoir of B. pertussis. In mice, macrophages and NK cells have a key role in confining B. pertussis to the respiratory tract. However, the mechanisms underlying this process, particularly during human infections, remain unclear. Here we characterized the activation of human macrophages and NK cells in response to B. pertussis and unraveled the role of inflammasomes in this process. NLRP3 inflammasome activation by B. pertussis in human macrophage-like THP-1 cells and primary monocyte-derived macrophages (mo-MΦ) was shown by the visualization of ASC-speck formation, pyroptosis, and the secretion of caspase-mediated IL-1β and IL-18. In contrast to macrophages, stimulation of human CD56+CD3- NK cells by B. pertussis alone did not result in activation of these cells. However, co-culture of B. pertussis-stimulated mo-MΦ and autologous NK cells resulted in high amounts of IFNγ secretion and an increased frequency of IL-2Rα+ and HLA-DR+ NK cells, indicating NK cell activation. This activation was significantly reduced upon inhibition of inflammasome activity or blocking of IL-18 in the mo-MΦ/NK cell co-culture. Furthermore, we observed increased secretion of proinflammatory cytokines in the B. pertussis-stimulated mo-MΦ/NK co-culture compared to the mo-MΦ single culture. Our results demonstrate that B. pertussis induces inflammasome activation in human macrophages and that the IL-18 produced by these cells is required for the activation of human NK cells, which in turn enhances the pro-inflammatory response to this pathogen. Our data provides a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms involved in the induction of innate immune responses against B. pertussis. These findings contribute to the knowledge required for the development of improved intervention strategies to control this highly contagious disease.
Keywords: Bordetella pertussis; NLRP3; crosstalk; human; inflammasome; innate immunity; interferon-gamma; interleukin-18.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differences in innate IFNγ and IL-17 responses to Bordetella pertussis between BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice: role of γδT cells, NK cells, and dendritic cells.Immunol Res. 2017 Dec;65(6):1139-1149. doi: 10.1007/s12026-017-8957-4. Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 29052125
-
Depletion of NK cells results in disseminating lethal infection with Bordetella pertussis associated with a reduction of antigen-specific Th1 and enhancement of Th2, but not Tr1 cells.Eur J Immunol. 2004 Sep;34(9):2579-88. doi: 10.1002/eji.200425092. Eur J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15307190
-
Interleukin-12 is produced by macrophages in response to live or killed Bordetella pertussis and enhances the efficacy of an acellular pertussis vaccine by promoting induction of Th1 cells.Infect Immun. 1996 Dec;64(12):5295-301. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.12.5295-5301.1996. Infect Immun. 1996. PMID: 8945580 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase-11 non-canonical inflammasome: a critical sensor of intracellular lipopolysaccharide in macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses.Immunology. 2017 Oct;152(2):207-217. doi: 10.1111/imm.12787. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Immunology. 2017. PMID: 28695629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complement evasion by Bordetella pertussis: implications for improving current vaccines.J Mol Med (Berl). 2015 Apr;93(4):395-402. doi: 10.1007/s00109-015-1259-1. Epub 2015 Feb 18. J Mol Med (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25686752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Innate Lymphoid Cells: Important Regulators of Host-Bacteria Interaction for Border Defense.Microorganisms. 2020 Sep 2;8(9):1342. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8091342. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32887435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bordetella pertussis-infected innate immune cells drive the anti-pertussis response of human airway epithelium.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 7;12(1):3622. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07603-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35256671 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical and Non-canonical Inflammasome Activation by Outer Membrane Vesicles Derived From Bordetella pertussis.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 20;11:1879. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01879. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32973778 Free PMC article.
-
Innate Lymphoid Cells and Natural Killer Cells in Bacterial Infections: Function, Dysregulation, and Therapeutic Targets.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Nov 5;11:733564. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.733564. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34804991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammasomes cross-talk with lymphocytes to connect the innate and adaptive immune response.J Adv Res. 2023 Dec;54:181-193. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.01.012. Epub 2023 Jan 18. J Adv Res. 2023. PMID: 36681114 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

