Contrasting the physiological effects of heliox and oxygen during exercise in a patient with advanced COPD
- PMID: 31508165
- PMCID: PMC6717618
- DOI: 10.1183/20734735.0197-2019
Contrasting the physiological effects of heliox and oxygen during exercise in a patient with advanced COPD
Abstract
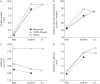
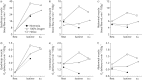
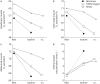
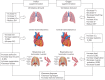
In COPD patients the ergogenic effect of heliox or oxygen breathing might be related both to improvements in ventilatory parameters (that lessen dyspnoea) and to enhanced oxygen delivery to respiratory and locomotor muscles http://bit.ly/2JlJBTc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Z. Louvaris has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: I. Vogiatzis has nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Updated 2014). www.goldcopd.org - PubMed
-
- Borg GA. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1982; 14: 377–381. - PubMed
-
- Louvaris Z, Vogiatzis I, Aliverti A, et al. . Blood flow does not redistribute from respiratory to leg muscles during exercise breathing heliox or oxygen in COPD. J Appl Physiol 2014; 117: 267–276. - PubMed
-
- Palange P, Crimi E, Pellegrino R, et al. . Supplemental oxygen and heliox: “new” tools for exercise training in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2005; 11: 145–148. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
