EFFECTS OF EXENDIN-4 ON ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM STRESS-MEDIATED INSULIN RESISTANCE IN 3T3-L1 ADIPOCYTES
- PMID: 31508171
- PMCID: PMC6711649
- DOI: 10.4183/aeb.2019.158
EFFECTS OF EXENDIN-4 ON ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM STRESS-MEDIATED INSULIN RESISTANCE IN 3T3-L1 ADIPOCYTES
Abstract
Objective: Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) is suspected as an important factor in the initiation of insulin resistance.
Aim: To explore the effects of exendin-4 (Ex-4) on the endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS)-mediated insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. In our study, 3T3-L1 adipocytes were pre-treated with ERS inhibitors tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA), Ex-4 and an ERS inducer tunicamycin (TM) then induced insulin resistance. Glucose consumption of the adipocytes was measured. Western blots determined the protein levels of ERS markers and insulin signaling pathway.
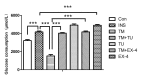
Results: TM treatment reduced insulin-stimulated glucose consumption by 19.7% in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. This repression was blunted by 24h pre-treatment with TUDCA or Ex-4. Ex-4 augmented insulin-stimulated glucose consumption in adipocytes by 14.9%. Western blotting showed that TM treatment significantly increased the ER stress markers including p-IRE, p-JNK, p-PERK, p-eIF2a and ATF6 expression, whereas 24h pre-treatment of adipocytes with TUDCA or Ex-4 alleviated the ER stress. Ex-4 alleviates ERS-induced insulin resistance by upregulating the expression of phosphorylated Akt.
Conclusion: ERs mediates insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, and exendin-4 significantly improves this insulin resistance.
Keywords: 3T3-L1 Adipocytes; ER stress; Exendin-4; insulin resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

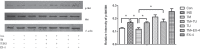
Similar articles
-
In vitro treatment of 3 T3-L1 adipocytes with recombinant Calcium/calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase IV (CaMKIV) limits ER stress and improves insulin sensitivity through inhibition of autophagy via the mTOR/CREB signaling pathway.BMC Endocr Disord. 2020 Jul 13;20(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12902-020-00589-2. BMC Endocr Disord. 2020. PMID: 32660483 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid-stimulating hormone induces insulin resistance in adipocytes via endoplasmic reticulum stress.Endocr Connect. 2024 Jul 15;13(8):e230302. doi: 10.1530/EC-23-0302. Print 2024 Aug 1. Endocr Connect. 2024. PMID: 38904465 Free PMC article.
-
FFA-induced adipocyte inflammation and insulin resistance: involvement of ER stress and IKKβ pathways.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2011 Mar;19(3):483-91. doi: 10.1038/oby.2010.200. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2011. PMID: 20829802
-
Tauroursodeoxycholic acid inhibits TNF-α-induced lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via the IRE-JNK-perilipin-A signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Apr;15(4):1753-1758. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6209. Epub 2017 Feb 16. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28260008
-
Excessive or sustained endoplasmic reticulum stress: one of the culprits of adipocyte dysfunction in obesity.Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Oct 7;15:20420188241282707. doi: 10.1177/20420188241282707. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 39381518 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High T3 Induces β-Cell Insulin Resistance via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Jul 22;2020:5287108. doi: 10.1155/2020/5287108. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32774144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2006;444(7121):840–846. - PubMed
-
- Ozcan U, Cao Q, Yilimaz E, Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Özdelen E, Tuncman G, Görg C. Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes. Science. 2004;306(5695):457–461. - PubMed
-
- Harding HP, Ron D. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the development of diabetes: a review. Diabetes. 2002;51(Suppl 3):S455–S461. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
