Current outcomes and treatment of tetralogy of Fallot
- PMID: 31508203
- PMCID: PMC6719677
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.17174.1
Current outcomes and treatment of tetralogy of Fallot
Abstract
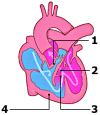
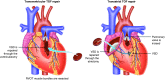
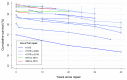
Tetralogy of Fallot (ToF) is the most common type of cyanotic congenital heart disease. Since the first surgical repair in 1954, treatment has continuously improved. The treatment strategies currently used in the treatment of ToF result in excellent long-term survival (30 year survival ranges from 68.5% to 90.5%). However, residual problems such as right ventricular outflow tract obstruction, pulmonary regurgitation, and (ventricular) arrhythmia are common and often require re-interventions. Right ventricular dysfunction can be seen following longstanding pulmonary regurgitation and/or stenosis. Performing pulmonary valve replacement or relief of pulmonary stenosis before irreversible right ventricular dysfunction occurs is important, but determining the optimal timing of pulmonary valve replacement is challenging for several reasons. The biological mechanisms underlying dysfunction of the right ventricle as seen in longstanding pulmonary regurgitation are poorly understood. Different methods of assessing the right ventricle are used to predict impending dysfunction. The atrioventricular, ventriculo-arterial and interventricular interactions of the right ventricle play an important role in right ventricle performance, but are not fully elucidated. In this review we present a brief overview of the history of ToF, describe the treatment strategies currently used, and outline the long-term survival, residual lesions, and re-interventions following repair. We discuss important remaining challenges and present the current state of the art regarding these challenges.
Keywords: Congenital Heart Disease; Fallot; Outcomes; Survival; Tetralogy.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Fallot ELA: Contribution à l’anatomie pathologique de la maladie bleue (cyanose cardiaque). Marseille Médical. 1888(25):77–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

