Discovery and characterization of a small-molecule enteropeptidase inhibitor, SCO-792
- PMID: 31508234
- PMCID: PMC6726858
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.517
Discovery and characterization of a small-molecule enteropeptidase inhibitor, SCO-792
Abstract
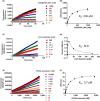
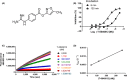
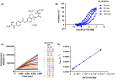
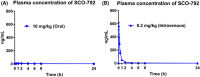
Enteropeptidase, localized into the duodenum brush border, is a key enzyme catalyzing the conversion of pancreatic trypsinogen proenzyme to active trypsin, thereby regulating protein digestion and energy homeostasis. We report the discovery and pharmacological profiles of SCO-792, a novel inhibitor of enteropeptidase. A screen employing fluorescence resonance energy transfer was performed to identify enteropeptidase inhibitors. Inhibitory profiles were determined by in vitro assays. To evaluate the in vivo inhibitory effect on protein digestion, an oral protein challenge test was performed in rats. Our screen identified a series of enteropeptidase inhibitors, and compound optimization resulted in identification of SCO-792, which inhibited enteropeptidase activity in vitro, with IC 50 values of 4.6 and 5.4 nmol/L in rats and humans, respectively. In vitro inhibition of enteropeptidase by SCO-792 was potentiated by increased incubation time, and the calculated Kinact/KI was 82 000/mol/L s. An in vitro dissociation assay showed that SCO-792 had a dissociation half-life of almost 14 hour, with a calculated koff rate of 0.047/hour, which suggested that SCO-792 is a reversible enteropeptidase inhibitor. In normal rats, a ≤4 hour prior oral dose of SCO-792 effectively inhibited plasma elevation of branched-chain amino acids in an oral protein challenge test, which indicated that SCO-792 effectively inhibited protein digestion in vivo. In conclusion, our new screen system identified SCO-792 as a potent and reversible inhibitor against enteropeptidase. SCO-792 slowly dissociated from enteropeptidase in vitro and inhibited protein digestion in vivo. Further study using SCO-792 could reveal the effects of inhibiting enteropeptidase on biological actions.
Keywords: FRET; SCO‐792; covalent; enteropeptidase.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was conducted with the financial support of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Ltd. Among the authors, M.S., I.M., S.I., H.Y., H.H., K.T., K.H., Y.M., M.W., K.T., M.S., J.S., and T.K. are/were employees of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd., and Y.M. and M.W. are employees of SCOHIA PHARMA, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of SCO-792, A Novel Enteropeptidase Inhibitor, In the Prevention of Post-Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Pancreatitis.Cureus. 2021 Mar 5;13(3):e13724. doi: 10.7759/cureus.13724. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33833935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SCO-792, an enteropeptidase inhibitor, improves disease status of diabetes and obesity in mice.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019 Oct;21(10):2228-2239. doi: 10.1111/dom.13799. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019. PMID: 31144422 Free PMC article.
-
Enteropeptidase inhibitor SCO-792 effectively prevents kidney function decline and fibrosis in a rat model of chronic kidney disease.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021 Mar 29;36(4):631-640. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa349. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021. PMID: 33351150 Free PMC article.
-
Enteropeptidase inhibition improves kidney function in a rat model of diabetic kidney disease.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021 Jan;23(1):86-96. doi: 10.1111/dom.14190. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021. PMID: 32893449 Free PMC article.
-
The role of enteropeptidase in the digestion of protein and its development in human fetal small intestine.Ciba Found Symp. 1979 Jan 16-18;(70):169-87. doi: 10.1002/9780470720530.ch10. Ciba Found Symp. 1979. PMID: 396133 Review.
Cited by
-
Cryo-EM structures reveal the activation and substrate recognition mechanism of human enteropeptidase.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 14;13(1):6955. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34364-9. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36376282 Free PMC article.
-
An Exploratory Randomized Trial of SCO-792, an Enteropeptidase Inhibitor, in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Albuminuria.Kidney Int Rep. 2022 Oct 8;8(1):115-125. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.10.006. eCollection 2023 Jan. Kidney Int Rep. 2022. PMID: 36644351 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of a Novel Series of 4-Guanidinobenzoate Derivatives as Enteropeptidase Inhibitors with Low Systemic Exposure for the Treatment of Obesity.J Med Chem. 2022 Jun 23;65(12):8456-8477. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00463. Epub 2022 Jun 10. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35686954 Free PMC article.
-
Role of SCO-792, A Novel Enteropeptidase Inhibitor, In the Prevention of Post-Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Pancreatitis.Cureus. 2021 Mar 5;13(3):e13724. doi: 10.7759/cureus.13724. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33833935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Global Status and Trends of Enteropeptidase: A Bibliometric Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 10;9:779722. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.779722. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35223895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zheng XL, Kitamoto Y, Sadler JE. Enteropeptidase, a type II transmembrane serine protease. Front Biosci. 2009;1:242‐249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

