Sonoporation of Cells by a Parallel Stable Cavitation Microbubble Array
- PMID: 31508275
- PMCID: PMC6724477
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.201900557
Sonoporation of Cells by a Parallel Stable Cavitation Microbubble Array
Abstract
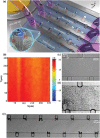
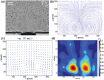
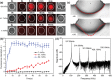
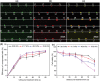
Sonoporation is a targeted drug delivery technique that employs cavitation microbubbles to generate transient pores in the cell membrane, allowing foreign substances to enter cells by passing through the pores. Due to the broad size distribution of microbubbles, cavitation events appear to be a random process, making it difficult to achieve controllable and efficient sonoporation. In this work a technique is reported using a microfluidic device that enables in parallel modulation of membrane permeability by an oscillating microbubble array. Multirectangular channels of uniform size are created at the sidewall to generate an array of monodispersed microbubbles, which oscillate with almost the same amplitude and resonant frequency, ensuring homogeneous sonoporation with high efficacy. Stable harmonic and high harmonic signals emitted by individual oscillating microbubbles are detected by a laser Doppler vibrometer, which indicates stable cavitation occurred. Under the influence of the acoustic radiation forces induced by the oscillating microbubble, single cells can be trapped at an oscillating microbubble surface. The sonoporation of single cells is directly influenced by the individual oscillating microbubble. The parallel sonoporation of multiple cells is achieved with an efficiency of 96.6 ± 1.74% at an acoustic pressure as low as 41.7 kPa.
Keywords: acoustic radiation force; membrane permeability; sonoporation; stable cavitation; ultrasound bioeffects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Control of Acoustic Cavitation for Efficient Sonoporation with Phase-Shift Nanoemulsions.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019 Mar;45(3):846-858. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2018.12.001. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 30638968 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional array of microbubbles sonoporation of cells in microfluidics.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Feb 14;12:1353333. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1353333. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38419723 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Cavitation Targeted Microbubble-Mediated Single-Cell Sonoporation.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Jan 11;13(1):113. doi: 10.3390/mi13010113. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35056278 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound and microbubble mediated therapeutic delivery: Underlying mechanisms and future outlook.J Control Release. 2020 Oct 10;326:75-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.06.008. Epub 2020 Jun 14. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32554041 Review.
-
Mechanisms underlying sonoporation: Interaction between microbubbles and cells.Ultrason Sonochem. 2020 Oct;67:105096. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105096. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Ultrason Sonochem. 2020. PMID: 32278246 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound-Responsive Nanocarriers for Breast Cancer Chemotherapy.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Sep 11;13(9):1508. doi: 10.3390/mi13091508. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36144131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional micro/nanobubbles for ultrasound medicine and visualizable guidance.Sci China Chem. 2021;64(6):899-914. doi: 10.1007/s11426-020-9945-4. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Sci China Chem. 2021. PMID: 33679901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selected Quality Parameters of Air-Dried Apples Pretreated by High Pressure, Ultrasounds and Pulsed Electric Field-A Comparison Study.Foods. 2021 Aug 20;10(8):1943. doi: 10.3390/foods10081943. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34441719 Free PMC article.
-
Transcranial focused ultrasound precise neuromodulation: a review of focal size regulation, treatment efficiency and mechanisms.Front Neurosci. 2024 Sep 5;18:1463038. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1463038. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39301015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moderate-Intensity Ultrasound-Triggered On-Demand Analgesia Nanoplatforms for Postoperative Pain Management.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Jul 23;17:3177-3189. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S367190. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35909815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paciotti G. F., Myer L., Weinreich D., Goia D., Pavel N., McLaughlin R. E., Tamarkin L., Drug Delivery 2004, 11, 169. - PubMed
-
- Li S., Huang L., Gene Ther. 1997, 4, 891. - PubMed
-
- Naldini L., Blomer U., Gallay P., Ory D., Mulligan R., Gage F. H., Verma I. M., Trono D., Science 1996, 272, 263. - PubMed
-
- Bennett J., Ashtari M., Wellman J., Marshall K. A., Cyckowski L. L., Chung D. C., McCague S., Pierce E. A., Chen Y., Bennicelli J. L., Zhu X., Ying G.‐S., Sun J., Wright J. F., Auricchio A., Simonelli F., Shindler K. S., Mingozzi F., High K. A., Maguire A. M., Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 120ra15. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
