Plain radiography findings to predict dislocation after total hip arthroplasty
- PMID: 31508301
- PMCID: PMC6718917
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jot.2018.12.003
Plain radiography findings to predict dislocation after total hip arthroplasty
Abstract
Background: With the improvements of modern surgical techniques and hip prosthesis, the causes for dislocation after total hip arthroplasty (THA) have changed. The aim of this retrospective analysis was to identify new plain radiography findings to predict dislocation after THA.
Methods: Five thousand five hundred thirteen consecutive primary THAs performed between January 2000 and December 2014 were reviewed through a nested case-control study design. Among them, 38 patients with 39 hip dislocations (dislocation group) were selected and matched to 78 hips in 78 patients without dislocation (control group). The factors that might influence the prosthetic stability were identified by univariate analyses, and a multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to determine the odds ratio of each factor.
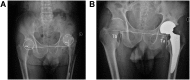
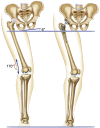
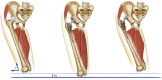
Results: The difference of the cup position was not statistically significant. The newly identified risk factors were the following: preoperative hip adduction deformity combined with limb lengthening of 2 cm postoperatively; a knee valgus combined with pelvic obliquity deformity and bilateral pathological hips.
Conclusions: Patients with soft tissue imbalance, across joint deformity around hips and bilateral pathological hips seem more predisposed to suffer from dislocation after THA. Appropriate surgical intervention strategies along with meticulously postoperative management may help preventing dislocation after THA.
The translational potential of this article: A better understanding of the probable causes of dislocation after THA proposed a new clinical application of plain radiography. This radiography-related clinical research may reveal the novel mechanism of dislocation after THA and new preventive measures.
Keywords: AD, Adduction deformity; ASA, American Society of Anesthesiologists; BMI, Body mass index; BP, Bilateral pathological hips; Case–control study; Dislocation; KV, Valgus deformity of the knee; MLL, Mild limb lengthening; OR, Odds ratios; PO, Pelvic obliquity; Risk factors; THA, Total hip arthroplasty; Total hip arthroplasty.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the rate of post-operative dislocation in patients with ipsilateral valgus knee deformity after primary total hip arthroplasty.Int Orthop. 2022 Jul;46(7):1507-1514. doi: 10.1007/s00264-022-05372-7. Epub 2022 Mar 20. Int Orthop. 2022. PMID: 35306569
-
Risk factors for dislocation after revision total hip arthroplasty with a dual-mobility cup. Matched case-control study (16 cases vs. 48 controls).Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019 Nov;105(7):1303-1309. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2019.01.020. Epub 2019 May 29. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 31153859
-
Dual-mobility or Constrained Liners Are More Effective Than Preoperative Bariatric Surgery in Prevention of THA Dislocation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016 Oct;474(10):2202-10. doi: 10.1007/s11999-016-4859-3. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016. PMID: 27130648 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors and modes of failure in the modern dual mobility implant. A systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Jun 14;22(1):541. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04404-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 34126990 Free PMC article.
-
Dual mobility total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of femoral neck fractures.Bone Joint J. 2020 Nov;102-B(11):1457-1466. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.102B11.BJJ-2020-0610.R2. Bone Joint J. 2020. PMID: 33135437
Cited by
-
Findings of preoperative patient risk factors to predict dislocation following total hip arthroplasty.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 May 15;13:1601997. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1601997. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40443733 Free PMC article.
-
Narrative Review of the Mechanism of Hip Prosthesis Dislocation and Methods to Reduce the Risk of Dislocation.Med Sci Monit. 2022 Jun 18;28:e935665. doi: 10.12659/MSM.935665. Med Sci Monit. 2022. PMID: 35715941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adverse effects of total hip arthroplasty on the hip abductor and adductor muscle lengths and moment arms during gait.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Aug 12;15(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01832-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32787875 Free PMC article.
-
Multivariable Analysis of Risk Factors Affecting Dislocation After Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty in Patients with Femoral Neck Fracture.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022 Feb 9;18:101-111. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S350213. eCollection 2022. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022. PMID: 35173434 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning Artificial Intelligence Model for Assessment of Hip Dislocation Risk Following Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty From Postoperative Radiographs.J Arthroplasty. 2021 Jun;36(6):2197-2203.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2021.02.028. Epub 2021 Feb 16. J Arthroplasty. 2021. PMID: 33663890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stroh D.A., Issa K., Johnson A.J., Delanois R.E., Mont M.A. Reduced dislocation rates and excellent functional outcomes with large-diameter femoral heads. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28:1415–1420. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

