Classification of the journal category "oral surgery" in the Scopus and the Science Citation Index Expanded: flaws and suggestions
- PMID: 31508350
- PMCID: PMC6728620
- DOI: 10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.4.186
Classification of the journal category "oral surgery" in the Scopus and the Science Citation Index Expanded: flaws and suggestions
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to evaluate the journal category "oral surgery" in Scopus and in the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE).
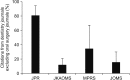
Materials and methods: The Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (JOMS), The Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons (JKAOMS), and The Journal of Prosthodontic Research (JPR) were selected from the Scopus list of journals as oral surgery journals. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (MPRS) was selected from PubMed as a Scopus oral surgery title. From these titles, 10 recently published articles were collected and used for reference analysis.
Results: The percentage of citations from oral surgery journals was 26.7%, 24.5%, and 40.1% for JKAOMS, MPRS, and JOMS, respectively. In total, 1.1% of JPR's citations were from oral surgery journals and significantly fewer from other journals (P<0.001). The percentage of citations from dentistry journals excluding oral surgery journals was 11.9%, 34.4%, and 15.8% for JKAOMS, MPRS, and JOMS, respectively. For JPR, 80.6% of citations were from dentistry journals and significantly more were from other journals (P<0.001).
Conclusion: Selected samples revealed that JPR is incorrectly classified as an oral surgery journal in Scopus. In addition, the scientific interaction among JKAOMS, MPRS, and JOMS was different to JPR in the reference analysis.
Keywords: Journal article; Journal impact factor; Oral cavity; Periodicals; Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The author is an editor of Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. That had no influence in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Chakraborty J, Pradhan D, Dutta HS, Nandi S, Chakraborty T. On good and bad intentions behind anomalous citation patterns among journals in computer sciences. Digital Libraries. 2018:arXiv:1807.10804v1. [cs.DL]
-
- Journal Search [Internet] Philadelphia (PA): Clarivate Analytics; [cited 2019 Jan 4]. Available from: http://mjl.clarivate.com/cgi-bin/jrnlst/jlsubcatg.cgi?PC=D.
-
- Sources [Internet] Amsterdam: Elsevier; [cited 2019 Jan 4]. Available from: https://www.scopus.com/sources.uri?zone=TopNavBar&origin=searchbasic.
-
- Ruela WS, de Almeida VL, Lima-Rivera LM, Santos PL, Porporatti AL, de Freitas PHL, et al. Does an association exist between the presence of lower third molar and mandibular angle fractures?: a meta-analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;76:34–45. - PubMed
-
- Lima TC, Bagordakis E, Falci SGM, Dos Santos CRR, Pinheiro MLP. Pre-emptive effect of dexamethasone and diclofenac sodium associated with codeine on pain, swelling, and trismus after third molar surgery: a split-mouth, randomized, triple-blind, controlled clinical trial. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;76:60–66. - PubMed

