The relationship between body mass index and preeclampsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31508571
- PMCID: PMC6718883
- DOI: 10.18502/ijrm.v17i7.4857
The relationship between body mass index and preeclampsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: One of the causes of maternal and fetal mortality and morbidity is pregnancy-induced hypertension, the most common form of which is preeclampsia that causes many complications for mother and fetus.
Objective: The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to determine the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and preeclampsia in Iran.
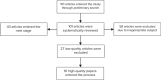
Materials and methods: Using valid keywords in the SID database, PubMed, Scopus, data obtained from all the articles, which were reviewed in Iran between 2000 and 2016, were combined using the meta-analysis method (random-effects model) and analyzed using STATA version 11.1.
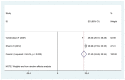
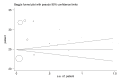
Results: A total number of 5,946 samples were enrolled in 16 studies with the mean BMI values of 25.13, 27.42, and 26.33 kg /m in the healthy, mild, and severe preeclamptic groups, respectively.
Conclusion: The results of this study revealed that there is a significant relationship between BMI and the risk of preeclampsia, so it can be said that BMI may be one of the ways to diagnose preeclampsia.
Keywords: Body mass index; Iran; Meta-analysis.; Preeclampsia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cuningham F., Leveno K., Bloom S., Hauth J., Gilstrap L., Katharine W. Williams Obstetrics. 22th. New York: Mccraw-Hill; 2005. Williams obstetrics; p. 768.
-
- Cunnigham FG., Gant NF., Leveno KJ., Larry C. Obstetrics. Journal of Midwifery Womens Health. 2010:48–369.
-
- Shah S., Gupta A. Gupta A. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Cardiol Clin. Vol. 37. 37: 345-354; 2019. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Cardiol Clin; pp. 345–354. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
