Genetic and phenotypic characterization of NKX6-2-related spastic ataxia and hypomyelination
- PMID: 31509304
- PMCID: PMC6946857
- DOI: 10.1111/ene.14082
Genetic and phenotypic characterization of NKX6-2-related spastic ataxia and hypomyelination
Abstract
Background and purpose: Hypomyelinating leukodystrophies are a heterogeneous group of genetic disorders with a wide spectrum of phenotypes and a high rate of genetically unsolved cases. Bi-allelic mutations in NKX6-2 were recently linked to spastic ataxia 8 with hypomyelinating leukodystrophy.
Methods: Using a combination of homozygosity mapping, exome sequencing, and detailed clinical and neuroimaging assessment a series of new NKX6-2 mutations in a multicentre setting is described. Then, all reported NKX6-2 mutations and those identified in this study were combined and an in-depth analysis of NKX6-2-related disease spectrum was provided.
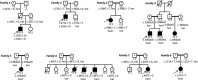
Results: Eleven new cases from eight families of different ethnic backgrounds carrying compound heterozygous and homozygous pathogenic variants in NKX6-2 were identified, evidencing a high NKX6-2 mutation burden in the hypomyelinating leukodystrophy disease spectrum. Our data reveal a phenotype spectrum with neonatal onset, global psychomotor delay and worse prognosis at the severe end and a childhood onset with mainly motor phenotype at the milder end. The phenotypic and neuroimaging expression in NKX6-2 is described and it is shown that phenotypes with epilepsy in the absence of overt hypomyelination and diffuse hypomyelination without seizures can occur.
Conclusions: NKX6-2 mutations should be considered in patients with autosomal recessive, very early onset of nystagmus, cerebellar ataxia with hypotonia that rapidly progresses to spasticity, particularly when associated with neuroimaging signs of hypomyelination. Therefore, it is recommended that NXK6-2 should be included in hypomyelinating leukodystrophy and spastic ataxia diagnostic panels.
Keywords: NKX6-2; SPAX8; hypomyelination; leukodystrophy; spastic ataxia 8.
© 2019 The Authors. European Journal of Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial or other conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Dorboz I, Aiello C, Simons C, et al Biallelic mutations in the homeodomain of NKX6‐2 underlie a severe hypomyelinating leukodystrophy. Brain 2017; 140: 2550–2556. - PubMed
-
- Anazi S, Maddirevula S, Salpietro V, et al Expanding the genetic heterogeneity of intellectual disability. Hum Genet 2017; 136: 1419–1429. - PubMed
-
- Baldi C, Bertoli‐Avella AM, Al‐Sannaa N, et al Expanding the clinical and genetic spectra of NKX6‐2‐related disorder. Clin Genet 2018; 93: 1087–1092. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- RAC#2120022/KFSHRC seed grant/International
- G1001253/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT104033/Z/14/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- RGP-VPP-301/Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University, Riyadh/International
- British Neurological Surveillance Unit (BNSU)/International
- MR/J004758/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0802760/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 14-MED2007-20/KACST Grant/International
- National Institute for Health Research (NIHR)/International
- Ataxia UK/International
- WT093205MA/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- K08 NS083739/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS106298/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- NS083739/NIH NINDS/International
- MR/S01165X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

