Controlling the Circadian Clock with High Temporal Resolution through Photodosing
- PMID: 31509406
- PMCID: PMC6787957
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.9b05445
Controlling the Circadian Clock with High Temporal Resolution through Photodosing
Abstract
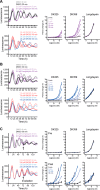
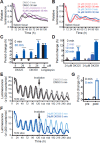
Circadian clocks, biological timekeepers that are present in almost every cell of our body, are complex systems whose disruption is connected to various diseases. Controlling cellular clock function with high temporal resolution in an inducible manner would yield an innovative approach for the circadian rhythm regulation. In the present study, we present structure-guided incorporation of photoremovable protecting groups into a circadian clock modifier, longdaysin, which inhibits casein kinase I (CKI). Using photodeprotection by UV or visible light (400 nm) as the external stimulus, we have achieved quantitative and light-inducible control over the CKI activity accompanied by an accurate regulation of circadian period in cultured human cells and mouse tissues, as well as in living zebrafish. This research paves the way for the application of photodosing in achieving precise temporal control over the biological timing and opens the door for chronophotopharmacology to deeper understand the circadian clock system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
High-throughput chemical screen identifies a novel potent modulator of cellular circadian rhythms and reveals CKIα as a clock regulatory kinase.PLoS Biol. 2010 Dec 14;8(12):e1000559. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000559. PLoS Biol. 2010. PMID: 21179498 Free PMC article.
-
Reversible modulation of circadian time with chronophotopharmacology.Nat Commun. 2021 May 26;12(1):3164. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23301-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34039965 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal separation of PER and CRY posttranslational regulation in the mammalian circadian clock.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Feb 4;111(5):2040-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323618111. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24449901 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Chemical Compounds to Identify the Regulatory Mechanisms of Vertebrate Circadian Clocks.Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(5):425-432. doi: 10.2174/1389450120666190926143120. Curr Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 31556855 Review.
-
Synchronization of the mammalian circadian timing system: Light can control peripheral clocks independently of the SCN clock: alternate routes of entrainment optimize the alignment of the body's circadian clock network with external time.Bioessays. 2015 Oct;37(10):1119-28. doi: 10.1002/bies.201500026. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Bioessays. 2015. PMID: 26252253 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Synchronized Circadian Clock Enhances Early Chondrogenesis.Cartilage. 2021 Dec;13(2_suppl):53S-67S. doi: 10.1177/1947603520903425. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Cartilage. 2021. PMID: 32059614 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic and chemical architecture of the mammalian circadian clock.Cell Chem Biol. 2023 Sep 21;30(9):1033-1052. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.08.014. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Cell Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37708890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatiotemporal Control Over Circadian Rhythms With Light.Med Res Rev. 2025 May;45(3):968-984. doi: 10.1002/med.22099. Epub 2025 Jan 5. Med Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 39757143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards medical imaging of drug photoactivation: Development of light responsive magnetic resonance imaging and chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast agents.Smart Mol. 2024 Jun 1;2(2):e20230029. doi: 10.1002/smo.20230029. eCollection 2024 Jun. Smart Mol. 2024. PMID: 40625803 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Application of Photocaged Isopropyl β-D-1-Thiogalactopyranoside for Light-Mediated Control of Bacterial Gene Expression.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2840:133-148. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4047-0_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39724349
References
-
- Hirota T.; Lee J. W.; Lewis W. G.; Zhang E. E.; Breton G.; Liu X.; Garcia M.; Peters E. C.; Etchegaray J.-P.; Traver D.; Schultz P. G.; Kay S. A. High-Throughput Chemical Screen Identifies a Novel Potent Modulator of Cellular Circadian Rhythms and Reveals CKIα as a Clock Regulatory Kinase. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8 (12), e1000559.10.1371/journal.pbio.1000559. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

