Risk of sepsis among patients with COPD treated with fixed combinations of inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting Beta2 agonists
- PMID: 31509517
- PMCID: PMC6756880
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.102217
Risk of sepsis among patients with COPD treated with fixed combinations of inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting Beta2 agonists
Abstract
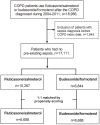
This study aimed to compare the effect of budesonide/formoterol and fluticasone/salmeterol on the risk and outcomes of sepsis in COPD patients. We conducted this study using the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database. We included COPD patients prescribed with budesonide/formoterol or fluticasone/salmeterol between 2004 and 2011. Outcomes including sepsis and mortality were measured. 10,267 COPD patients who received fluticasone/salmeterol and 6,844 patients who received budesonide/formoterol were enrolled into this study and then subsequence were adjusted by propensity score weighting. The incidence of sepsis was 5.74 and 4.99 per 100 person-years for the patients receiving fluticasone/salmeterol and budesonide/formoterol, respectively. Fluticasone/salmeterol was associated with higher risk of sepsis (aHR, 1.15; 95%CI, 1.07-1.24) and septic shock (aHR, 1.14; 95%CI, 1.01-1.29) than budesonide/formoterol. Besides, fluticasone/salmeterol was associated with higher risk of death (aHR, 1.090; 95%CI, 1.01-1.18) than budesonide/formoterol. Patients receiving fluticasone/salmeterol had a significant higher risk of sepsis related respiratory organ dysfunction, lower respiratory tract infection, genitourinary tract infection, bacteremia and skin infection. In conclusion, long-term treatment with budesonide/formoterol was associated with lower rates of sepsis and deaths than fluticasone/salmeterol in patients with COPD.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; inhaled corticosteroids; long-acting beta2 agonists; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Risk of active tuberculosis among COPD patients treated with fixed combinations of long-acting beta2 agonists and inhaled corticosteroids.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Sep 25;20(1):706. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05440-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32977747 Free PMC article.
-
Severe exacerbation and pneumonia in COPD patients treated with fixed combinations of inhaled corticosteroid and long-acting beta2 agonist.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017 Aug 21;12:2477-2485. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S139035. eCollection 2017. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017. PMID: 28860742 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of budesonide/formoterol and fluticasone/salmeterol combinations in COPD patients: findings from a real-world analysis in an Italian setting.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016 Nov 4;11:2749-2755. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S114554. eCollection 2016. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016. PMID: 27853362 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing a fixed combination of budesonide/formoterol with other inhaled corticosteroid plus long-acting beta-agonist combinations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a review.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2019 Nov;13(11):1087-1094. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2019.1665514. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2019. PMID: 31498714 Review.
-
Differences in the efficacy and safety among inhaled corticosteroids (ICS)/long-acting beta2-agonists (LABA) combinations in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): Role of ICS.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Feb;30:44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2014.10.006. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25445928 Review.
Cited by
-
Capsule Commentary on Griffith et al., Overuse and Misuse of Inhaled Corticosteroids Among Veterans with COPD: a Cross-Sectional Study Evaluating Targets for De-implementation.J Gen Intern Med. 2020 Mar;35(3):979. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-05598-z. J Gen Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 31898129 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sepsis in Aging Populations: A Review of Risk Factors, Diagnosis, and Management.Cureus. 2024 Dec 2;16(12):e74973. doi: 10.7759/cureus.74973. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39744263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying Common Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets between COPD and Sepsis: A Bioinformatics and Machine Learning Approach.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025 May 28;20:1761-1786. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S510846. eCollection 2025. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025. PMID: 40453984 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review on long-term adverse effects of inhaled corticosteroids in the treatment of COPD.Eur Respir Rev. 2021 Jun 23;30(160):210075. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0075-2021. Print 2021 Jun 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2021. PMID: 34168063 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of active tuberculosis among COPD patients treated with fixed combinations of long-acting beta2 agonists and inhaled corticosteroids.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Sep 25;20(1):706. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05440-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32977747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, Alvarado M, Anderson HR, Anderson LM, et al.. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012; 380:2095–128. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Calverley P, Pauwels R, Vestbo J, Jones P, Pride N, Gulsvik A, Anderson J, Maden C, and TRial of Inhaled STeroids ANd long-acting beta2 agonists study group. Combined salmeterol and fluticasone in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2003; 361:449–56. 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12459-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical