Polyamine biosynthesis in Xenopus laevis: the xlAZIN2/xlODC2 gene encodes a lysine/ornithine decarboxylase
- PMID: 31509528
- PMCID: PMC6738921
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218500
Polyamine biosynthesis in Xenopus laevis: the xlAZIN2/xlODC2 gene encodes a lysine/ornithine decarboxylase
Abstract
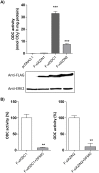
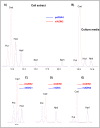
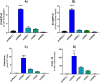
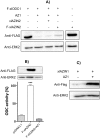
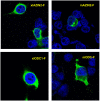
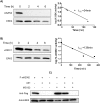
Ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) is a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of polyamines, organic cations that are implicated in many cellular processes. The enzyme is regulated at the post-translational level by an unusual system that includes antizymes (AZs) and antizyme inhibitors (AZINs). Most studies on this complex regulatory mechanism have been focused on human and rodent cells, showing that AZINs (AZIN1 and AZIN2) are homologues of ODC but devoid of enzymatic activity. Little is known about Xenopus ODC and its paralogues, in spite of the relevance of Xenopus as a model organism for biomedical research. We have used the information existing in different genomic databases to compare the functional properties of the amphibian ODC1, AZIN1 and AZIN2/ODC2, by means of transient transfection experiments of HEK293T cells. Whereas the properties of xlODC1 and xlAZIN1 were similar to those reported for their mammalian orthologues, the former catalyzing the decarboxylation of L-ornithine preferentially to that of L-lysine, xlAZIN2/xlODC2 showed important differences with respect to human and mouse AZIN2. xlAZIN2 did not behave as an antizyme inhibitor, but it rather acts as an authentic decarboxylase forming cadaverine, due to its higher affinity to L-lysine than to L-ornithine as substrate; so, in accordance with this, it should be named as lysine decarboxylase (LDC) or lysine/ornithine decarboxylase (LODC). In addition, AZ1 stimulated the degradation of xlAZIN2 by the proteasome, but the removal of the 21 amino acid C-terminal tail, with a sequence quite different to that of mouse or human ODC, made the protein resistant to degradation. Collectively, our results indicate that in Xenopus there is only one antizyme inhibitor (xlAZIN1) and two decarboxylases, xlODC1 and xlLDC, with clear preferences for L-ornithine and L-lysine, respectively.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
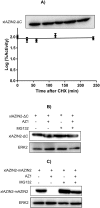
Similar articles
-
The mouse Gm853 gene encodes a novel enzyme: Leucine decarboxylase.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018 Mar;1862(3):365-376. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.11.007. Epub 2017 Nov 4. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018. PMID: 29108956
-
Mouse ornithine decarboxylase-like gene encodes an antizyme inhibitor devoid of ornithine and arginine decarboxylating activity.J Biol Chem. 2006 Oct 13;281(41):30896-906. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602840200. Epub 2006 Aug 17. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16916800
-
Influence of ornithine decarboxylase antizymes and antizyme inhibitors on agmatine uptake by mammalian cells.Amino Acids. 2015 May;47(5):1025-34. doi: 10.1007/s00726-015-1931-3. Epub 2015 Feb 6. Amino Acids. 2015. PMID: 25655388
-
Regulation of polyamine biosynthesis by antizyme and some recent developments relating the induction of polyamine biosynthesis to cell growth. Review.Biosci Rep. 1985 Mar;5(3):189-204. doi: 10.1007/BF01119588. Biosci Rep. 1985. PMID: 3893559 Review.
-
Antizyme inhibitor family: biological and translational research implications.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 2;22(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01445-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38169396 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mahogunin Ring Finger 1 regulates pigmentation by controlling the pH of melanosomes in melanocytes and melanoma cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec 18;79(1):47. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04053-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34921635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen S. A Guide to the Polyamines. 1997. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

