Anatomical analysis of antebrachial cutaneous nerve distribution pattern and its clinical implications for sensory reconstruction
- PMID: 31509579
- PMCID: PMC6738927
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222335
Anatomical analysis of antebrachial cutaneous nerve distribution pattern and its clinical implications for sensory reconstruction
Erratum in
-
Correction: Anatomical analysis of antebrachial cutaneous nerve distribution pattern and its clinical implications for sensory reconstruction.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 10;14(10):e0223916. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223916. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31600348 Free PMC article.
Abstract
This study aimed to reveal the distribution pattern of antebrachial cutaneous nerves and provide a morphological basis for sensory reconstruction during flap transplantation. Forearm specimens containing skin and subcutaneous fat were obtained from 24 upper extremities of 12 adult cadavers. Cutaneous nerves were visualized using modified Sihler's staining. Then the data was used to show the distribution pattern and innervation area of the forearm cutaneous nerve. The anterior branch of lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve innervates 26% of the medial anterior forearm; the posterior branch innervates 38.21% of the lateral anterior forearm and 24.46% of the lateral posterior forearm. The anterior branch of medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve innervates the medial aspect of the forearm covering 27.67% of the anterior region; the posterior branch the lateral part of the forearm covering 7.67% and 34.75% of the anterior and posterior regions, respectively. The posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve covers 41.04% of the posterior forearm. Coaptations were found between the branches of these cutaneous nerves. The relatively dense secondary nerve branches were found in the middle 1/3 of the lateral anterior forearm and the middle 1/3 of the medial posterior forearm. The relatively dense tertiary nerve branches were the middle 1/3 and lower 1/3 of the medial anterior forearm. The intradermal nerve branches were the relatively dense in the middle 1/3 of the medial anterior and lateral posterior forearm. The middle 1/3 of the medial and lateral forearm had the relatively dense total nerve branches. These results can be used sensory matching while designing forearm flaps for reconstruction surgeries to obtain improved recovery of sensory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
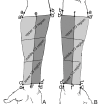
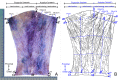


Similar articles
-
Sihler's staining of the cutaneous nerves of the leg and its implications for sensory reconstruction.Clin Anat. 2021 May;34(4):565-573. doi: 10.1002/ca.23613. Epub 2020 May 15. Clin Anat. 2021. PMID: 32319700
-
Optimizing Innervation in Radial Forearm Phalloplasty: Consider the Posterior Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2023 Jan 1;151(1):202-206. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000009771. Epub 2022 Dec 26. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2023. PMID: 36576827 Review.
-
Cutaneous innervation of the distal forearm and hand - Minimizing complication rate by defining danger zones for surgical approaches.Ann Anat. 2018 Nov;220:38-50. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2018.06.007. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Ann Anat. 2018. PMID: 30048757
-
Triceps and cutaneous radial nerve branches investigated via an axillary anterior arm approach: new findings in a fresh-cadaver anatomical study.J Neurosurg. 2021 Oct 8;136(5):1424-1433. doi: 10.3171/2021.4.JNS2169. Print 2022 May 1. J Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 34624848
-
Anatomy of the Posterior Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve, Revisited.J Hand Surg Am. 2020 Apr;45(4):360.e1-360.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2019.08.011. Epub 2019 Oct 22. J Hand Surg Am. 2020. PMID: 31653469 Review.
Cited by
-
Correction: Anatomical analysis of antebrachial cutaneous nerve distribution pattern and its clinical implications for sensory reconstruction.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 10;14(10):e0223916. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223916. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31600348 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical effects of neurocutaneous vascular flap innervated by terminal branch of lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve in repairing finger tip or finger pulp wounds of the thumb].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2021 Aug 20;37(8):758-763. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20200607-00298. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34404163 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Research trends and perspectives on immediate facial reanimation in radical parotidectomy (Review).Biomed Rep. 2023 Sep 21;19(5):81. doi: 10.3892/br.2023.1663. eCollection 2023 Nov. Biomed Rep. 2023. PMID: 37881603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Surgical Approach to a Medial Epicondylectomy in Cubital Tunnel Syndrome.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025 Jun 10;13(6):e6861. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006861. eCollection 2025 Jun. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025. PMID: 40496993 Free PMC article.
-
The Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve Is a Low-Morbidity Alternative to the Standard Sural Nerve Autograft.Hand (N Y). 2025 Jun;20(4):542-548. doi: 10.1177/15589447231218459. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Hand (N Y). 2025. PMID: 38179958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Masear VR, Meyer RD, Pichora DR. Surgical anatomy of the medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve. J Hand Surg Am. 1989; 14: 267–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

