Job Satisfaction Mediates the Association between Perceived Disability and Work Productivity in Migraine Headache Patients
- PMID: 31510071
- PMCID: PMC6765904
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16183341
Job Satisfaction Mediates the Association between Perceived Disability and Work Productivity in Migraine Headache Patients
Abstract
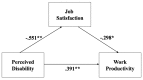
Migraine headache is the cause of an estimated 250,000,000 lost days from work or school every year and is often associated with decreased work productivity. The aim of this cross-sectional study was to assess the relationship between perceived disability, job satisfaction and work productivity in patients affected by chronic migraineurs. Participants were 98 consecutive adult outpatients admitted to the Regional Referral Headache Centre of the Sant'Andrea Hospital in Rome, Italy. Patients were administered the Italian Perceived Disability Scale, The Quality of Life Enjoyment and Satisfaction Questionnaire-Work Subscale and The Endicott Work Productivity Scale. Perceived disability is significantly associated with job satisfaction and work productivity. Job satisfaction is significantly related to work productivity and mediates the association between perceived disability and work productivity in patients affected by chronic migraineurs. Our results confirm that patients suffering from migraine headaches who have negative perceptions of their disability are less satisfied with their job, which in turn, decreases their work productivity.
Keywords: health psychology; job satisfaction; migraine; perceived disability; work productivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overattachment and perceived disability in chronic migraineurs.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013 Jul;115(7):954-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.09.029. Epub 2012 Oct 27. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013. PMID: 23107164
-
Illness Perception and Job Satisfaction in Patients Suffering from Migraine Headaches: Trait Anxiety and Depressive Symptoms as Potential Mediators.Headache. 2019 Jan;59(1):46-55. doi: 10.1111/head.13461. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Headache. 2019. PMID: 30548860
-
Difficulties in work activities and the pervasive effect over disability in patients with episodic and chronic migraine.Neurol Sci. 2015 May;36 Suppl 1:9-11. doi: 10.1007/s10072-015-2130-4. Neurol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26017503
-
Identification of work accommodations and interventions associated with work productivity in adults with migraine: A scoping review.Cephalalgia. 2021 May;41(6):760-773. doi: 10.1177/0333102420977852. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Cephalalgia. 2021. PMID: 33302697
-
Migraine heterogeneity. Disability, pain intensity, and attack frequency and duration.Neurology. 1994 Jun;44(6 Suppl 4):S24-39. Neurology. 1994. PMID: 8008223 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of COVID-19 on Tourist Satisfaction with B&B in Zhejiang, China: An Importance-Performance Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 May 25;17(10):3747. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17103747. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32466326 Free PMC article.
-
Headache in Workers: A Matched Case-Control Study.Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2022 Dec 7;12(12):1852-1866. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe12120130. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2022. PMID: 36547031 Free PMC article.
-
Migraine Among University Students: Prevalence, Characteristics, and Sociodemographic Influences.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Jul 18;13(14):1746. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13141746. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40724771 Free PMC article.
-
Job satisfaction and its associated factors among health care workers in Saint Paul's Hospital Millennium Medical College, Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 25;20(6):e0326496. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326496. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40561006 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of sleep and disability associated with headache: migraine versus tension-type headache: A comparative study.Ann Afr Med. 2023 Jan-Mar;22(1):11-17. doi: 10.4103/aam.aam_241_21. Ann Afr Med. 2023. PMID: 36695217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386:743–800. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stovner L.J., Nichols E., Steiner T.J., Abd-Allah F., Abdelalim A., Al-Raddadi R.M., Ansha M.G., Barac A., Bensenor I.M., Doan L.P., et al. Global, regional, and national burden of migraine and tension-type headache, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17:954–976. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30322-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical