Dual roles and therapeutic potential of Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in pancreatic cancer: a systematic review
- PMID: 31511020
- PMCID: PMC6740038
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-019-0435-2
Dual roles and therapeutic potential of Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in pancreatic cancer: a systematic review
Abstract
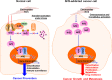
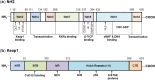
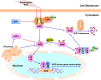
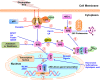
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is one of the most fatal diseases with a very high rate of metastasis and low rate of survival. Despite the advances in understanding this devastating disease, PC still accounts for 3% of all cancers and causes almost 7% of death of cancer patients. Recent studies have demonstrated that the transcription factor nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and its key negative regulator Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) are dysregulated in PC and the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway is an emerging target for PC prevention and therapy. Indeed, Nrf2 plays an either tumor-suppressive or promoting function in PC, which depends on the developmental stages of the disease and the cellular context. Several natural-product Nrf2 activators have been developed to prevent pancreatic carcinogenesis, while the Nrf2 inhibitors have been examined for their efficacy in inhibiting PC growth and metastasis and reversing chemoresistance. However, further preclinical and clinical studies for determining the effectiveness and safety of targeting the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway for PC prevention and therapy are warranted. In this review, we comprehensively discuss the dual roles of the Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway in PC as well as the current targeting strategies and known activators and inhibitors of Nrf2. We also propose new strategies that may be used to address the current issues and develop more specific and more effective Nrf2 activator/inhibitors for PC prevention and therapy.
Keywords: Keap1; Nrf2; Pancreatic cancer; Prevention and therapy; Small molecule activators and inhibitors; Tumor-suppressive and promoting roles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent progress in Keap1-Nrf2 protein-protein interaction inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Sep 15;202:112532. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112532. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32668381 Review.
-
Emerging Substrate Proteins of Kelch-like ECH Associated Protein 1 (Keap1) and Potential Challenges for the Development of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the Keap1-Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2) Protein-Protein Interaction.J Med Chem. 2020 Aug 13;63(15):7986-8002. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01865. Epub 2020 Apr 8. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32233486 Review.
-
The Keap1-Nrf2 protein-protein interaction: A suitable target for small molecules.Drug Discov Today Technol. 2017 Jun;24:11-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2017. PMID: 29233294 Review.
-
Keap1-Nrf2 signalling in pancreatic cancer.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Aug;65:288-99. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.06.017. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26117456 Review.
-
The Keap1-Nrf2-ARE Pathway As a Potential Preventive and Therapeutic Target: An Update.Med Res Rev. 2016 Sep;36(5):924-63. doi: 10.1002/med.21396. Epub 2016 May 18. Med Res Rev. 2016. PMID: 27192495 Review.
Cited by
-
Whole-exome mutational landscape of metastasis in patient-derived hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Genes Dis. 2020 May 15;7(3):380-391. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.05.003. eCollection 2020 Sep. Genes Dis. 2020. PMID: 32884992 Free PMC article.
-
3,4‑Dihydroxyacetophenone attenuates oxidative stress‑induced damage to HUVECs via regulation of the Nrf2/HO‑1 pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Jun;25(6):199. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12715. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 35475506 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Preclinical Cancer Studies under Physioxia to Enhance Clinical Translation.Cancer Res. 2022 Dec 2;82(23):4313-4321. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-2311. Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36169928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Terphenyllin Suppresses Orthotopic Pancreatic Tumor Growth and Prevents Metastasis in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Apr 8;11:457. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00457. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32322210 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming hypoxia-induced resistance of pancreatic and lung tumor cells by disrupting the PERK-NRF2-HIF-axis.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jan 13;12(1):82. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03319-7. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33441543 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

