Effects of Helicobacter pylori treatment and vitamin and garlic supplementation on gastric cancer incidence and mortality: follow-up of a randomized intervention trial
- PMID: 31511230
- PMCID: PMC6737461
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.l5016
Effects of Helicobacter pylori treatment and vitamin and garlic supplementation on gastric cancer incidence and mortality: follow-up of a randomized intervention trial
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effects of Helicobacter pylori treatment, vitamin supplementation, and garlic supplementation in the prevention of gastric cancer.
Design: Blinded randomized placebo controlled trial.
Setting: Linqu County, Shandong province, China.
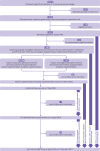
Participants: 3365 residents of a high risk region for gastric cancer. 2258 participants seropositive for antibodies to H pylori were randomly assigned to H pylori treatment, vitamin supplementation, garlic supplementation, or their placebos in a 2×2×2 factorial design, and 1107 H pylori seronegative participants were randomly assigned to vitamin supplementation, garlic supplementation, or their placebos in a 2×2 factorial design.
Interventions: H pylori treatment with amoxicillin and omeprazole for two weeks; vitamin (C, E, and selenium) and garlic (extract and oil) supplementation for 7.3 years (1995-2003).
Main outcome measures: Primary outcomes were cumulative incidence of gastric cancer identified through scheduled gastroscopies and active clinical follow-up through 2017, and deaths due to gastric cancer ascertained from death certificates and hospital records. Secondary outcomes were associations with other cause specific deaths, including cancers or cardiovascular disease.
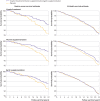
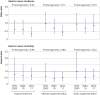
Results: 151 incident cases of gastric cancer and 94 deaths from gastric cancer were identified during 1995-2017. A protective effect of H pylori treatment on gastric cancer incidence persisted 22 years post-intervention (odds ratio 0.48, 95% confidence interval 0.32 to 0.71). Incidence decreased significantly with vitamin supplementation but not with garlic supplementation (0.64, 0.46 to 0.91 and 0.81, 0.57 to 1.13, respectively). All three interventions showed significant reductions in gastric cancer mortality: fully adjusted hazard ratio for H pylori treatment was 0.62 (95% confidence interval 0.39 to 0.99), for vitamin supplementation was 0.48 (0.31 to 0.75), and for garlic supplementation was 0.66 (0.43 to 1.00). Effects of H pylori treatment on both gastric cancer incidence and mortality and of vitamin supplementation on gastric cancer mortality appeared early, but the effects of vitamin supplementation on gastric cancer incidence and of garlic supplementation only appeared later. No statistically significant associations were found between interventions and other cancers or cardiovascular disease.
Conclusions: H pylori treatment for two weeks and vitamin or garlic supplementation for seven years were associated with a statistically significant reduced risk of death due to gastric cancer for more than 22 years. H pylori treatment and vitamin supplementation were also associated with a statistically significantly reduced incidence of gastric cancer.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00339768.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/coi_disclosure.pdf (available on request from the corresponding author) and declare: no support from any organization for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- You WC, Blot WJ, Chang YS, et al. Diet and high risk of stomach cancer in Shandong, China. Cancer Res 1988;48:3518-23. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Blot WJ, You WC, et al. Helicobacter pylori antibodies in relation to precancerous gastric lesions in a high-risk Chinese population. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 1996;5:627-30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
