What have we learned from basic science studies on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?
- PMID: 31511255
- PMCID: PMC9488501
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0029-2019
What have we learned from basic science studies on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?
Abstract
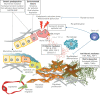
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a fatal age-related lung disease characterised by progressive and irreversible scarring of the lung. Although the details are not fully understood, there has been tremendous progress in understanding the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, which has led to the identification of many new potential therapeutic targets. In this review we discuss several of these advances with a focus on genetic susceptibility and cellular senescence primarily affecting epithelial cells, activation of profibrotic pathways, disease-enhancing fibrogenic cell types and the role of the remodelled extracellular matrix.
Copyright ©ERS 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: T. Yanagihara reports personal fees from Prometic, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: S. Sato reports grants from Canadian Institute for Health Research, during the conduct of the study. Conflict of interest: C. Upagupta reports grants from Canadian Institute for Health Research, during the conduct of the study. Conflict of interest: M. Kolb reports grants from Canadian Institute for Health Research, during the conduct of the study; grants and personal fees from Roche, Boehringer Ingelheim and Prometic, grants from Actelion, Respivert and Alkermes, and personal fees from Genoa, Indalo and Third Pole, outside the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Hopkins RB, Burke N, Fell C, et al. . Epidemiology and survival of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis from national data in Canada. Eur Respir J 2016; 48: 187–195. - PubMed
-
- Raghu G, Chen S-Y, Yeh W-S, et al. . Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in US Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older: incidence, prevalence, and survival, 2001–11. Lancet Respir Med 2014; 2: 566–572. - PubMed
-
- Ley B, Collard HR, King TE. Clinical course and prediction of survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011; 183: 431–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
