Serological Array-in-Well Multiplex Assay Reveals a High Rate of Respiratory Virus Infections and Reinfections in Young Children
- PMID: 31511367
- PMCID: PMC6739493
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.00447-19
Serological Array-in-Well Multiplex Assay Reveals a High Rate of Respiratory Virus Infections and Reinfections in Young Children
Abstract
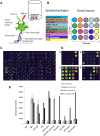
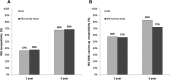
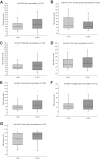
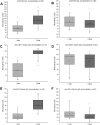
Serological assays are used to diagnose and characterize host immune responses against microbial pathogens. Microarray technologies facilitate high-throughput immunoassays of antibody detection against multiple pathogens simultaneously. To improve survey of influenza A virus (IAV), influenza B virus (IBV), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and adenovirus (AdV) antibody levels, we developed a microarray consisting of IAV H1N1, IAV H1N1pdm09 (vaccine), IAV H3N2, IBV Victoria, IBV Yamagata, RSV, AdV type 5 hexon protein, and control antigens printed on the bottom of a microtiter plate well. Bound IgG antibodies were detected with anti-human IgG-coated photon-upconverting nanoparticles and measured with a photoluminescence imager. The performance of the microarray immunoassay (MAIA) was evaluated with serum samples (n = 576) collected from children (n = 288) at 1 and 2 years of age and tested by standard enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) for antibodies to IAV vaccine and RSV. EIAs and MAIA showed substantial to almost perfect agreement (Cohen's κ, 0.62 to 0.83). Applying MAIA, we found seroprevalences of 55% for IAV H1N1, 54% for IAV vaccine, 30% for IAV H3N2, 24% for IBV Victoria, 25% for IBV Yamagata, 38% for RSV, and 26% for AdV in 1-year-old children (n = 768). By the age of 2 years, IgG seropositivity rates (n = 714) increased to 74% for IAV H1N1, 71% for IAV vaccine, 49% for IAV H3N2, 47% for IBV Yamagata, 49% for IBV Victoria, 68% for RSV, and 58% for AdV. By analyzing increases in antibody levels not biased by vaccinations, we found a reinfection rate of 40% for RSV and 31% for AdV in children between 1 and 2 years of age.IMPORTANCE The multiplex immunoassay was successfully used to simultaneously detect antibodies against seven different viruses. The developed serological microarray is a new promising tool for diagnostic, epidemiological, and seroprevalence analyses of virus infections.
Keywords: adenoviruses; immunoassays; influenza; influenza vaccines; microarray; multiplex; respiratory syncytial virus; upconversion luminescence.
Copyright © 2019 Kazakova et al.
Figures



References
-
- Jääskeläinen AJ, Viitala SM, Kurkela S, Hepojoki S, Sillanpää H, Kallio-Kokko H, Bergström T, Suni J, Närvänen A, Vapalahti O, Vaheri A. 2014. Performance of a multiplexed serological microarray for the detection of antibodies against central nervous system pathogens. J Microbiol Methods 100:27–31. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2014.02.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feron D, Charlier C, Gourain V, Garderet L, Coste-Burel M, Le Pape P, Weigel P, Jacques Y, Hermouet S, Bigot-Corbel E. 2013. Multiplexed infectious protein microarray immunoassay suitable for the study of the specificity of monoclonal immunoglobulins. Anal Biochem 433:202–209. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2012.10.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mezzasoma L, Bacarese-Hamilton T, Di Cristina M, Rossi R, Bistoni F, Crisanti A. 2002. Antigen microarrays for serodiagnosis of infectious diseases. Clin Chem 48:121–130. - PubMed
-
- Lochhead MJ, Todorof K, Delaney M, Ives JT, Greef C, Moll K, Rowley K, Vogel K, Myatt C, Zhang X-Q, Logan C, Benson C, Reed S, Schooley RT. 2011. Rapid multiplexed immunoassay for simultaneous serodiagnosis of HIV-1 and coinfections. J Clin Microbiol 49:3584–3590. doi:10.1128/JCM.00970-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

