Putative link between Polo-like kinases (PLKs) and Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling in transformed and primary human immune cells
- PMID: 31511529
- PMCID: PMC6739412
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-49017-z
Putative link between Polo-like kinases (PLKs) and Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling in transformed and primary human immune cells
Abstract
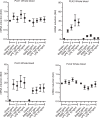
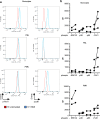
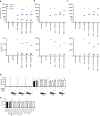
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are important sentinels of bacterial and viral infection and thus fulfil a critical sensory role in innate immunity. Polo-like kinases (PLKs), a five membered family of Ser/Thr protein kinases, have long been studied for their role in mitosis and thus represent attractive therapeutic targets in cancer therapy. Recently, PLKs were implicated in TLR signaling in mice but the role of PLKs in TLR signaling in untransformed primary immune cells has not been addressed, even though PLK inhibitors are in clinical trials. We here identified several phospho-serine and phospho-threonine residues in the known TLR pathway kinases, Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) 2 and IRAK4. These sites lie in canonical polo-box motifs (PBM), sequence motifs known to direct recruitment of PLKs to client proteins. Interestingly, PLK1 was phosphorylated and PLK 2 and 3 mRNA induced upon TLR stimulation in primary immune cells, respectively. In whole blood, PLK inhibition disparately affected TLR mediated cytokine responses in a donor- and inhibitor-dependent fashion. Collectively, PLKs may thus potentially interface with TLR signaling in humans. We propose that temporary PLK inhibitor-mediated blockade of TLR-signaling in certain patients receiving such inhibitors during cancer treatment may cause adverse effects such as an increased risk of infections due to a then compromised ability of the TLR recognition system to sense and initiate cytokine responses to invading microbes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is involved in toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated TNF-α production in monocytic THP-1 cells.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 18;8(10):e78832. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078832. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24205328 Free PMC article.
-
Non-mitotic functions of polo-like kinases in cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Jan;1875(1):188467. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188467. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33171265 Review.
-
Modelling the Functions of Polo-Like Kinases in Mice and Their Applications as Cancer Targets with a Special Focus on Ovarian Cancer.Cells. 2021 May 12;10(5):1176. doi: 10.3390/cells10051176. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34065956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress with polo-like kinase (PLK) inhibitors: a patent review (2018-present).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2024 Sep;34(9):789-806. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2024.2379924. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2024. PMID: 38994687 Review.
-
Interleukin 1/Toll-like receptor-induced autophosphorylation activates interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase 4 and controls cytokine induction in a cell type-specific manner.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 11;289(15):10865-10875. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.544809. Epub 2014 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24567333 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of polo-like kinase 1 as a therapeutic target in murine lupus.Clin Transl Immunology. 2022 Jan 6;11(1):e1362. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1362. eCollection 2022. Clin Transl Immunology. 2022. PMID: 35024139 Free PMC article.
-
PLK1 in cancer therapy: a comprehensive review of immunomodulatory mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 19;16:1602752. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1602752. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40612941 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kawai, T. & Akira, S. Toll-like receptor and RIG-I-like receptor signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci1143, 1–20, NYAS1143020 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

