Online Health Information Seeking Among US Adults: Measuring Progress Toward a Healthy People 2020 Objective
- PMID: 31513756
- PMCID: PMC6832079
- DOI: 10.1177/0033354919874074
Online Health Information Seeking Among US Adults: Measuring Progress Toward a Healthy People 2020 Objective
Abstract
Objective: During the past decade, the availability of health information online has increased dramatically. We assessed progress toward the Healthy People 2020 (HP2020) health communication and health information technology objective of increasing the proportion of health information seekers who easily access health information online.
Methods: We used data from 4 administrations of the Health Information National Trends Survey (HINTS 2008-2017) (N = 18 103). We conducted multivariable logistic regression analysis to evaluate trends over time in experiences with accessing health information and to examine differences by sociodemographic variables (sex, age, race/ethnicity, education, income, metropolitan status) separately for those who used the internet (vs other information sources) during their most recent search for health information.
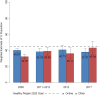
Results: Among US adults who looked for health information and used the internet for their most recent search, the percentage who reported accessing health information without frustration was stable during the study period (from 37.2% in 2008 to 38.5% in 2017). Accessing information online without frustration was significantly and independently associated with age 35-49 (vs age 18-34) (odds ratio [OR] = 1.34; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.03 -1.73), non-Hispanic black (vs non-Hispanic white) race/ethnicity (OR = 2.15; 95% CI, 1.55-2.97), and annual household income <$20 000 (vs >$75 000) (OR = 0.66; 95% CI, 0.47-0.93). The percentage of adults who used an information source other than the internet and reported accessing health information online without frustration ranged from 31.3% in 2008 to 42.7% in 2017. Survey year 2017 (vs 2008) (OR = 1.61; 95% CI, 1.09-2.35) and high school graduate education (vs college graduate) (OR = 0.69; 95% CI, 0.49-0.97) were significantly and independently associated with accessing health information without frustration from sources other than the internet.
Conclusions: The percentage of online health information seekers reporting easily accessing health information did not meet the HP2020 objective. Continued efforts are needed to enable easy access to online health information among diverse populations.
Keywords: Healthy People programs; access to information; frustration; health communication; internet.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Percheski C, Hargittai E. Health information-seeking in the digital age. J Am Coll Health. 2011;59(5):379–386. doi:10.1080/07448481.2010.513406 - PubMed
-
- Fox S. Health topics: 80% of internet users look for health information online. 2011. http://www.pewresearch.org/science. Accessed September 1, 2018.
-
- Prestin A, Vieux SN, Chou WY. Is online health activity alive and well or flatlining? Findings from 10 years of the Health Information National Trends Survey. J Health Commun. 2015;20(7):790–798. doi:10.1080/10810730.2015.1018590 - PubMed
-
- Rice RE. Influences, usage, and outcomes of internet health information searching: multivariate results from the Pew surveys. Int J Med Inform. 2006;75(1):8–28. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2005.07.032 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

