Anti-Tumor Potential of IMP Dehydrogenase Inhibitors: A Century-Long Story
- PMID: 31514446
- PMCID: PMC6770829
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11091346
Anti-Tumor Potential of IMP Dehydrogenase Inhibitors: A Century-Long Story
Abstract
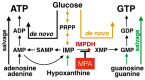
The purine nucleotides ATP and GTP are essential precursors to DNA and RNA synthesis and fundamental for energy metabolism. Although de novo purine nucleotide biosynthesis is increased in highly proliferating cells, such as malignant tumors, it is not clear if this is merely a secondary manifestation of increased cell proliferation. Suggestive of a direct causative effect includes evidence that, in some cancer types, the rate-limiting enzyme in de novo GTP biosynthesis, inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH), is upregulated and that the IMPDH inhibitor, mycophenolic acid (MPA), possesses anti-tumor activity. However, historically, enthusiasm for employing IMPDH inhibitors in cancer treatment has been mitigated by their adverse effects at high treatment doses and variable response. Recent advances in our understanding of the mechanistic role of IMPDH in tumorigenesis and cancer progression, as well as the development of IMPDH inhibitors with selective actions on GTP synthesis, have prompted a reappraisal of targeting this enzyme for anti-cancer treatment. In this review, we summarize the history of IMPDH inhibitors, the development of new inhibitors as anti-cancer drugs, and future directions and strategies to overcome existing challenges.
Keywords: GTP; IMPDH; IMPDH inhibitors; anti-tumor; mycophenolic acid; purine synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

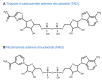
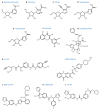
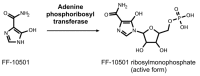
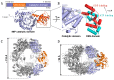
References
-
- Kofuji S., Hirayama A., Eberhardt A.O., Kawaguchi R., Sugiura Y., Sampetrean O., Ikeda Y., Warren M., Sakamoto N., Kitahara S., et al. IMP dehydrogenase-2 drives aberrant nucleolar activity and promotes tumorigenesis in glioblastoma. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019;21:1003–1014. doi: 10.1038/s41556-019-0363-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Collart F.R., Chubb C.B., Mirkin B.L., Huberman E. Increased inosine-5′-phosphate dehydrogenase gene expression in solid tumor tissues and tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1992;52:5826–5828. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

