The miR-205-5p/BRCA1/RAD17 Axis Promotes Genomic Instability in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas
- PMID: 31514456
- PMCID: PMC6771082
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11091347
The miR-205-5p/BRCA1/RAD17 Axis Promotes Genomic Instability in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas
Erratum in
-
Correction: Valenti et al. The miR-205-5p/BRCA1/RAD17 Axis Promotes Genomic Instability in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cancers 2019, 11, 1347.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 25;17(7):1089. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071089. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227598 Free PMC article.
Abstract
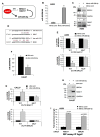
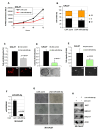
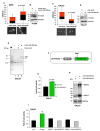
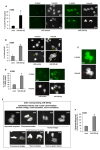
Defective DNA damage response (DDR) is frequently associated with tumorigenesis. Abrogation of DDR leads to genomic instability, which is one of the most common characteristics of human cancers. TP53 mutations with gain-of-function activity are associated with tumors under high replicative stress, high genomic instability, and reduced patient survival. The BRCA1 and RAD17 genes encode two pivotal DNA repair proteins required for proper cell-cycle regulation and maintenance of genomic stability. We initially evaluated whether miR-205-5p, a microRNA (miRNA) highly expressed in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), targeted BRCA1 and RAD17 expression. We found that, in vitro and in vivo, BRCA1 and RAD17 are targets of miR-205-5p in HNSCC, leading to inefficient DNA repair and increased chromosomal instability. Conversely, miR-205-5p downregulation increased BRCA1 and RAD17 messenger RNA (mRNA) levels, leading to a reduction in in vivo tumor growth. Interestingly, miR-205-5p expression was significantly anti-correlated with BRCA1 and RAD17 targets. Furthermore, we documented that miR-205-5p expression was higher in tumoral and peritumoral HNSCC tissues than non-tumoral tissues in patients exhibiting reduced local recurrence-free survival. Collectively, these findings unveil miR-205-5p's notable role in determining genomic instability in HNSCC through its selective targeting of BRCA1 and RAD17 gene expression. High miR-205-5p levels in the peritumoral tissues might be relevant for the early detection of minimal residual disease and pre-cancer molecular alterations involved in tumor development.
Keywords: DNA repair; HNSCC; genomic instability; miRNA; mutant p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Correction: Valenti et al. The miR-205-5p/BRCA1/RAD17 Axis Promotes Genomic Instability in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cancers 2019, 11, 1347.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 25;17(7):1089. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071089. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227598 Free PMC article.
-
Gain of function mutant p53 proteins cooperate with E2F4 to transcriptionally downregulate RAD17 and BRCA1 gene expression.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 20;6(8):5547-66. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2587. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25650659 Free PMC article.
-
miR-96-5p targets PTEN expression affecting radio-chemosensitivity of HNSCC cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Mar 29;38(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1119-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30925916 Free PMC article.
-
Role of microRNA-138 as a potential tumor suppressor in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2013;303:357-85. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407697-6.00009-X. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23445815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of SESN1, UHRF1BP1, and miR-377-3p as prognostic markers in mutated TP53 squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Cancer Biol Ther. 2017 Oct 3;18(10):775-782. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1373212. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Cancer Biol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28886272 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miRNA dysregulation is an emerging modulator of genomic instability.Semin Cancer Biol. 2021 Nov;76:120-131. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.05.004. Epub 2021 May 9. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021. PMID: 33979676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Modifications in Head and Neck Cancer.Biochem Genet. 2020 Apr;58(2):213-244. doi: 10.1007/s10528-019-09941-1. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Biochem Genet. 2020. PMID: 31712935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiRNA-Based Therapies for Lung Cancer: Opportunities and Challenges?Biomolecules. 2023 May 23;13(6):877. doi: 10.3390/biom13060877. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polo-like kinase 2 targeting as novel strategy to sensitize mutant p53-expressing tumor cells to anticancer treatments.J Mol Med (Berl). 2024 Dec;102(12):1485-1501. doi: 10.1007/s00109-024-02499-5. Epub 2024 Oct 31. J Mol Med (Berl). 2024. PMID: 39480521
-
Correction: Valenti et al. The miR-205-5p/BRCA1/RAD17 Axis Promotes Genomic Instability in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cancers 2019, 11, 1347.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 25;17(7):1089. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071089. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227598 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sigal A., Rotter V. Oncogenic mutations of the p53 tumor suppressor: The demons of the guardian of the genome. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6788–6793. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

