Synthesis and evaluation of the anti-hepatitis B virus activity of 4'-Azido-thymidine analogs and 4'-Azido-2'-deoxy-5-methylcytidine analogs: structural insights for the development of a novel anti-HBV agent
- PMID: 31514570
- PMCID: PMC8191380
- DOI: 10.1080/15257770.2019.1664749
Synthesis and evaluation of the anti-hepatitis B virus activity of 4'-Azido-thymidine analogs and 4'-Azido-2'-deoxy-5-methylcytidine analogs: structural insights for the development of a novel anti-HBV agent
Abstract
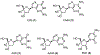
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a major worldwide health problem that requires the development of improved antiviral therapies. Here, a series of 4'-Azido-thymidine/4'-Azido-2'-deoxy-5-methylcytidine derivatives (6, 10-15) were synthesized, and their anti-HBV activities evaluated. Compounds 10-15 were synthesized via an SNAr reaction of 18, in which the 4-position of the thymine moiety was activated as the 2,4,6-triisopropylbenzenesulfonate. Compounds 11-15 showed no antiviral activity. However, 4'-Azido thymidine (6) and 4'-Azido-2'-deoxy-5-methylcytidine (10) displayed significant anti-HBV activity (EC50 = 0.63 and 5.99 µM, respectively) with no detectable cytotoxicity against MT-2 cells up to 100 µM.
Keywords: 4′-azido nucleoside; Anti-HBV nucleoside; modified pyrimidines.
Figures
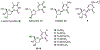
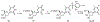
Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of new N(4)-Substituted 2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-4'-azido cytidine derivatives as potent anti-HBV agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Aug 28;101:103-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.06.030. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Eur J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26119991
-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of new 2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-4'-triazole cytidine nucleosides as potent antiviral agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2013 May;63:739-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.02.042. Epub 2013 Mar 24. Eur J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23570720
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2',3'-dideoxy-L-pyrimidine nucleosides as potential antiviral agents against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV).J Med Chem. 1994 Mar 18;37(6):798-803. doi: 10.1021/jm00032a013. J Med Chem. 1994. PMID: 8145230
-
Comparative evaluation of L-Fd4C and related nucleoside analogs as promising antiviral agents.Curr Med Chem. 2002 May;9(9):899-912. doi: 10.2174/0929867024606696. Curr Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 11966452 Review.
-
Recent progress in potential anti-hepatitis B virus agents: Structural and pharmacological perspectives.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Mar 10;147:205-217. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.02.001. Epub 2018 Feb 5. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29438889 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetics of 4'-cyano-2'-deoxyguanosine, a novel nucleoside analog inhibitor of the resistant hepatitis B virus, in a rat model of chronic kidney disease.J Infect Chemother. 2021 May;27(5):702-706. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2020.12.014. Epub 2020 Dec 30. J Infect Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33386259 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral nucleoside analogs.Chem Heterocycl Compd (N Y). 2021;57(4):326-341. doi: 10.1007/s10593-021-02912-8. Epub 2021 May 14. Chem Heterocycl Compd (N Y). 2021. PMID: 34007086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO fact sheet. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs204/en/
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
