Dentin dysplasia Type I: A rare case report
- PMID: 31516254
- PMCID: PMC6714252
- DOI: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_132_19
Dentin dysplasia Type I: A rare case report
Abstract
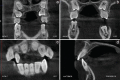
Dentin dysplasia (DD) is an uncommon developmental disturbance affecting dentin, resulting in enamel with atypical dentin formation and abnormal pulpal morphology. Type I (radicular) and Type II (coronal) are the two types of DD. Type I is more common, and both types include single or multiple teeth in primary and permanent dentition. Combinations of both types have also been described in literature. Four distinct forms of Type I and one form of Type II were identified. This case report documents one such rarity of DD in an 11-year-old female with clinical and radiographical findings and management aspects.
Keywords: Atypical dentin; dental anomaly; dentin dysplasia; pulp obliteration; pulp stones; rootless teeth.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures