Effect of morphine and a low dose of ketamine on the T cells of patients with refractory cancer pain in vitro
- PMID: 31516618
- PMCID: PMC6732974
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.10750
Effect of morphine and a low dose of ketamine on the T cells of patients with refractory cancer pain in vitro
Abstract
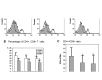
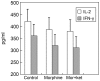
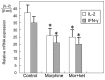
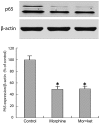
The combination of morphine and ketamine is considered safe and efficacious in many patients. However, a considerable number of immunomodulatory effects have been reported to be produced by both morphine and ketamine. The aim of the present study was to assess the direct effect of morphine and a low dose of ketamine on the T cells of patients with refractory cancer pain in vitro. Venous blood was obtained from patients with refractory cancer pain and peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated using the Ficoll-Hypaque density gradient method. Anti-CD3 beads were used to isolate T cells by positive selection. Subsequently, the T cells were treated with vehicle, 200 ng/ml of morphine or 200 ng/ml of morphine + 100 ng/ml ketamine for 24 h, following which the cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28. Flow cytometric analysis of CD3+ T cells, and interleukin (IL)-2 and interferon (IFN)-γ in the supernatant, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR analysis for the detection of IL-2 and IFN-γ and western blotting for the detection of p65 nuclear factor (NF)-κB were performed. In vitro, the CD4+ and CD8+ T cell counts, CD4+/CD8+ ratio, secretion of IL-2 and IFN-γ in the supernatant, mRNA expression levels of IL-2 and IFN-γ and expression of p65 NF-κB were significantly decreased following treatment with morphine and morphine + ketamine, compared with results in the control group (all P<0.05). However, there was no significant difference between treatment with morphine and that with morphine + ketamine. Treatment with morphine + ketamine in vitro decreased the immune functions of patients with refractory cancer pain, although the effect of treatment with morphine and a low dose of ketamine did not differ significantly from that with morphine treatment alone.
Keywords: T cells; cancer pain; interferon-γ; interleukin-2; ketamine; morphine; nuclear factor-κB.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
