Effect of 5-Aza-2'-Deoxycytidine in Comparison to Valproic Acid and Trichostatin A on Histone Deacetylase 1, DNA Methyltransferase 1, and CIP/KIP Family (p21, p27, and p57) Genes Expression, Cell Growth Inhibition, and Apoptosis Induction in Colon Cancer SW480 Cell Line
- PMID: 31516890
- PMCID: PMC6712896
- DOI: 10.4103/abr.abr_91_19
Effect of 5-Aza-2'-Deoxycytidine in Comparison to Valproic Acid and Trichostatin A on Histone Deacetylase 1, DNA Methyltransferase 1, and CIP/KIP Family (p21, p27, and p57) Genes Expression, Cell Growth Inhibition, and Apoptosis Induction in Colon Cancer SW480 Cell Line
Abstract
Background: Cancer initiation and progression depends on genetic and epigenetic alterations such as DNA methylation and histone modifications. Hypermethylation and deacetylation of the CIP/KIP family (p21, p27, and p57) lead to tumorigenesis. Our previous study indicated that DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) inhibitor and histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors can inhibit cell growth and induce apoptosis. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine (5-Aza-CdR) in comparison to valproic acid (VPA) and trichostatin A (TSA) on HDAC1, DNMT1, and CIP/KIP family (p21, p27, and p57) genes expression, cell growth inhibition, and apoptosis induction in colon cancer SW480 cell line.
Materials and methods: The effect of the compounds on the cell viability was measured by MTT assay. The expression of HDAC1, DNMT1, and CIP/KIP family (p21, p27, and p57) genes was evaluated by real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). For the detection of cell apoptosis, apoptotic cells were examined by the Annexin V-FITC/PI detection kit.
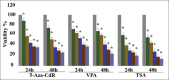
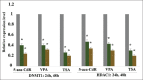
Results: The results of MTT assay indicated that 5-Aza-CdR, VPA, and TSA significantly inhibited cell growth (P < 0.002, P < 0.001, and P < 0.001, respectively). The results of real-time RT-PCR demonstrated that all compounds significantly down-regulated DNMT1 and HDAC1, and up-regulated p21, p27, and p57 genes expression. The result of flow cytometry assay revealed that all agents induced apoptosis significantly.
Conclusion: 5-Aza-CdR, VPA, and TSA can significantly downregulate DNMT1 and HDAC1 and up-regulate p21, p27, and p57 genes expression through which enhance cell apoptosis and cell growth inhibition in colon cancer.
Keywords: 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine; cancer; trichostatin A; valproic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kanai Y, Ushijima S, Kondo Y, Nakanishi Y, Hirohashi S. DNA methyltransferase expression and DNA methylation of CPG Islands and Peri-centromeric satellite regions in human colorectal and stomach cancers. Int J Cancer. 2001;91:205–12. - PubMed
-
- Higashijima J, Kurita N, Miyatani T, Yoshikawa K, Morimoto S, Nishioka M, et al. Expression of histone deacetylase 1 and metastasis-associated protein 1 as prognostic factors in colon cancer. Oncol Rep. 2011;26:343–8. - PubMed
-
- Park MT, Lee SJ. Cell cycle and cancer. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2003;36:60–5. - PubMed
-
- Chim CS, Wong AS, Kwong YL. Epigenetic inactivation of the CIP/KIP cell-cycle control pathway in acute leukemias. Am J Hematol. 2005;80:282–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

