Topical minocycline formulations: Evaluation and comparison of dermal uptake efficacy
- PMID: 31517274
- PMCID: PMC6733297
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2019.100009
Topical minocycline formulations: Evaluation and comparison of dermal uptake efficacy
Abstract
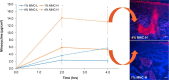
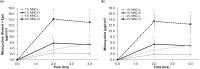
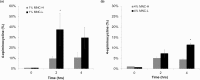
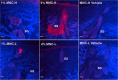
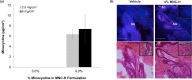
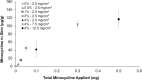
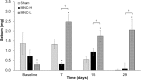
Acne vulgaris is a clinically distinct skin condition with evidence suggesting that inflammation plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of this disorder. Treatment of severe inflammatory acne often involves the use of oral antibiotics, sometimes in combination with topical products. Oral antibiotics often result in systemic side effects and the risks of antibiotic resistance, but no commercial topical minocycline is currently available. We have developed a unique, stable, hydrophilic topical gel formulation with fully solubilized minocycline (MNC-H). Minocycline delivered in our hydrophilic gel remained more stable in situ, resulting in less degradation product (4-epiminocycline) than a lipophilic formulation (MNC-L). The hydrophilic nature of our formulation enabled 2-3 fold increase in delivery into the skin ex vivo compared to a lipophilic counterpart, mostly seen in the epidermis and pilosebaceous units. The lipophilic formulation also appeared to be more occlusive, resulting in higher sebum production in minipigs, which may exacerbate acne vulgaris. As our results indicate, a 1, 2% minocycline hydrophilic gel may deliver sufficient drug (>15 μg/g) to potentially demonstrate clinical efficacy. These findings suggest that topical hydrophilic minocycline gel may provide a novel tool for topical acne therapy.
Keywords: Acne; Anti-inflammatory; Anti-microbial; BPX-01, 2% topical hydrophilic minocycline gel; Dermal; Hydrophilicity; MNC-H, topical hydrophilic minocycline gel formulations; MNC-L, topical lipophilic minocycline formulations; Skin; Tetracycline class; Transepidermal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Review of Systemic Minocycline Side Effects and Topical Minocycline as a Safer Alternative for Treating Acne and Rosacea.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Jun 22;10(7):757. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10070757. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34206485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BPX-01 Minocycline Topical Gel Shows Promise for the Treatment of Moderate-to-severe Inflammatory Acne Vulgaris.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018 Nov;11(11):25-35. Epub 2018 Nov 1. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 30588271 Free PMC article.
-
Treating Acne With Topical Antibiotics: Current Obstacles and the Introduction of Topical Minocycline as a New Treatment Option.J Drugs Dermatol. 2019 Mar 1;18(3):240-244. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30909327
-
Formulation and Profile of FMX101 4% Minocycline Topical Foam for the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020 Apr;13(4):14-21. Epub 2020 Apr 1. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 33144907 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating FMX-101 as a promising therapeutic for the treatment of acne.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 May;21(7):741-746. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1721461. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32037906 Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of Systemic Minocycline Side Effects and Topical Minocycline as a Safer Alternative for Treating Acne and Rosacea.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Jun 22;10(7):757. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10070757. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34206485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fractional microporation-guided delivery of nanoencapsulated drugs for enhanced cutaneous and follicular absorption: a comparison of ablative laser and radiofrequency microneedling.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 May 29. doi: 10.1007/s13346-025-01885-x. Online ahead of print. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40439860
References
-
- Alexis A., Del Rosso J.Q., Desai S.R., Downie J.B., Draelos Z.D., Feser C., Forconi R., Fowler J.F., Jr., Gold M., Kaufman-Janette J., Lain E., Lee M., Ling M., Shambran A.T., Werschler P., Daniels A.M. BPX-01 minocycline topical gel shows promise for the treatment of moderate-to-severe inflammatory acne vulgaris. J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2018;11(11):25–35. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bode G., Clausing P., Gervais F., Loegsted J., Luft J., Nogues V., Sims J. Steering group of the RETHINK Project The utility of the minipig as an animal model in regulatory toxicology. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Meth. 2010;62(3):196–220. - PubMed
-
- Dash A., Somnath S., Tolman J. Academic Press; Boston MA: 2014. Pharmaceutics: Basic Principles and Application to Pharmacy Practice.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

