Development and Comparison of Complementary Methods to Study Potential Skin and Inhalational Exposure to Pathogens During Personal Protective Equipment Doffing
- PMID: 31517983
- PMCID: PMC6761368
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciz616
Development and Comparison of Complementary Methods to Study Potential Skin and Inhalational Exposure to Pathogens During Personal Protective Equipment Doffing
Abstract
Background: Fluorescent tracers are often used with ultraviolet lights to visibly identify healthcare worker self-contamination after doffing of personal protective equipment (PPE). This method has drawbacks, as it cannot detect pathogen-sized contaminants nor airborne contamination in subjects' breathing zones.
Methods: A contamination detection/quantification method was developed using 2-µm polystyrene latex spheres (PSLs) to investigate skin contamination (via swabbing) and potential inhalational exposure (via breathing zone air sampler). Porcine skin coupons were used to estimate the PSL swabbing recovery efficiency and limit of detection (LOD). A pilot study with 5 participants compared skin contamination levels detected via the PSL vs fluorescent tracer methods, while the air sampler quantified potential inhalational exposure to PSLs during doffing.
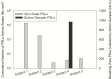
Results: Average PSL skin swab recovery efficiency was 40% ± 29% (LOD = 1 PSL/4 cm2 of skin). In the pilot study, all subjects had PSL and fluorescent tracer skin contamination. Two subjects had simultaneously located contamination of both types on a wrist and hand. However, for all other subjects, the PSL method enabled detection of skin contamination that was not detectable by the fluorescent tracer method. Hands/wrists were more commonly contaminated than areas of the head/face (57% vs 23% of swabs with PSL detection, respectively). One subject had PSLs detected by the breathing zone air sampler.
Conclusions: This study provides a well-characterized method that can be used to quantitate levels of skin and inhalational contact with simulant pathogen particles. The PSL method serves as a complement to the fluorescent tracer method to study PPE doffing self-contamination.
Keywords: doffing self-contamination; exposure assessment; inhalational exposure; methods development; personal protective equipment doffing.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




References
-
- Frieden TR, Damon I, Bell BP, Kenyon T, Nichol S. Ebola 2014—new challenges, new global response and responsibility. N Engl J Med 2014; 371:1177–80. - PubMed
-
- Courage KH. How did a Dallas nurse catch Ebola? Available at: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/how-did-a-dallas-nurse-catch-.... Accessed 1 February 2019.
-
- Alhmidi H, Koganti S, Tomas ME, Cadnum JL, Jencson A, Donskey CJ. A pilot study to assess use of fluorescent lotion in patient care simulations to illustrate pathogen dissemination and train personnel in correct use of personal protective equipment. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 2016; 5:40. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Casanova LM, Teal LJ, Sickbert-Bennett EE, et al. . CDC Prevention Epicenters Program Assessment of self-contamination during removal of personal protective equipment for Ebola patient care. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2016; 37:1156–61. - PubMed

