ERα-targeted endocrine therapy, resistance and the role of GPER
- PMID: 31518595
- PMCID: PMC6859199
- DOI: 10.1016/j.steroids.2019.108493
ERα-targeted endocrine therapy, resistance and the role of GPER
Abstract
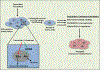
Endocrine therapy is an effective option for the treatment of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα)-positive breast cancers. Unfortunately, a large fraction of women relapse with endocrine-resistant tumors. The presence of constitutively active ERα mutants, found in a subset of relapse tumors, is thought to be an important endocrine resistance mechanism and has prompted the search for more effective anti-hormone drugs that can effectively inhibit these mutant versions of the receptor. The G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) is also thought to contribute to the development of endocrine resistance, in part, due to its activation by clinically used selective estrogen receptor modulators and downregulators (SERMs/SERDs). Therefore, next-generation drugs should be screened for potential activity towards GPER. Here, we highlight the need for truly ERα-selective SERMs and SERDs that do not cross-react with GPER for the treatment of ERα-positive breast cancers.
Keywords: Breast cancer; ERα; Endocrine resistance; GPER; SERD; SERM.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
E.R.P. is an inventor on U.S. Patent Nos. 7,875,721 and 8,487,100 for GPER-selective ligands and imaging agents and U.S. Patent No. 10,251,870 and pending patents for applications of GPER-selective ligands.
Figures

References
-
- Nilsson S, Makela S, Treuter E, Tujague M, Thomsen J, Andersson G, Enmark E, Pettersson K, Warner M, Gustafsson JA, Mechanisms of estrogen action, Physiological reviews 81(4) (2001) 1535–65. - PubMed
-
- Jensen EV, DeSombre ER, Estrogen-receptor interaction, Science 182(4108) (1973) 126–34. - PubMed
-
- Revankar CM, Cimino DF, Sklar LA, Arterburn JB, Prossnitz ER, A transmembrane intracellular estrogen receptor mediates rapid cell signaling, Science 307(5715) (2005) 1625–30. - PubMed
-
- Dahlman-Wright K, Cavailles V, Fuqua SA, Jordan VC, Katzenellenbogen JA, Korach KS, Maggi A, Muramatsu M, Parker MG, Gustafsson JA, International Union of Pharmacology. LXIV. Estrogen receptors, Pharmacological reviews 58(4) (2006) 773–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

