Favorable Alleles of GRAIN-FILLING RATE1 Increase the Grain-Filling Rate and Yield of Rice
- PMID: 31519786
- PMCID: PMC6836814
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.19.00413
Favorable Alleles of GRAIN-FILLING RATE1 Increase the Grain-Filling Rate and Yield of Rice
Abstract
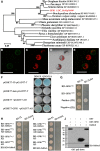
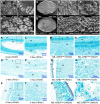
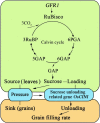
Hybrid rice (Oryza sativa) has been cultivated commercially for 42 years in China. However, poor grain filling still limits the development of hybrid japonica rice. We report here the map-based cloning and characterization of the GRAIN-FILLING RATE1 (GFR1) gene present at a major-effect quantitative trait locus. We elucidated and confirmed the function of GFR1 via genetic complementation experiments and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9) gene editing in combination with genetic and molecular biological analyses. In addition, we conducted haplotype association analysis to mine the elite alleles of GFR1 among 117 rice accessions. We observed that GFR1 was constitutively expressed and encoded a membrane-localized protein. The allele of the rice accession Ludao (GFR1 Ludao) improved the grain-filling rate of rice by increasing Rubisco initial activity in the Calvin cycle. Moreover, the increased expression of the cell wall invertase gene OsCIN1 in the near isogenic line NIL-GFR1 Ludao promoted the unloading of Suc during the rice grain-filling stage. A yeast two-hybrid assay indicated that the Rubisco small subunit interacts with GFR1, possibly in the regulation of the rice grain-filling rate. Evaluation of the grain-filling rate and grain yield of F1 plants harboring GFR1 Ludao and the alleles of 20 hybrids widely cultivated commercially confirmed that favorable alleles of GFR1 can be used to further improve the grain-filling rate of hybrid japonica rice.
© 2019 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enhanced Expression of QTL qLL9/DEP1 Facilitates the Improvement of Leaf Morphology and Grain Yield in Rice.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 17;20(4):866. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040866. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30781568 Free PMC article.
-
Time-course association mapping of the grain-filling rate in rice (Oryza sativa L.).PLoS One. 2015 Mar 19;10(3):e0119959. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119959. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25789629 Free PMC article.
-
An-1 encodes a basic helix-loop-helix protein that regulates awn development, grain size, and grain number in rice.Plant Cell. 2013 Sep;25(9):3360-76. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.113589. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 24076974 Free PMC article.
-
Control of grain size in rice.Plant Reprod. 2018 Sep;31(3):237-251. doi: 10.1007/s00497-018-0333-6. Epub 2018 Mar 10. Plant Reprod. 2018. PMID: 29523952 Review.
-
Applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 System for Rice Grain Quality Improvement: Perspectives and Opportunities.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 19;20(4):888. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040888. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30791357 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An in situ approach to characterizing photosynthetic gas exchange of rice panicle.Plant Methods. 2020 Jul 6;16:92. doi: 10.1186/s13007-020-00633-1. eCollection 2020. Plant Methods. 2020. PMID: 32647532 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic dissection of grain morphology and yield components in a wheat line with defective grain filling.Theor Appl Genet. 2023 Jul 1;136(7):165. doi: 10.1007/s00122-023-04410-1. Theor Appl Genet. 2023. PMID: 37392240
-
Transcriptome Analysis Provides Insights into Grain Filling in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 16;21(14):5031. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145031. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32708737 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis Provides Insights into the Heterosis of Yield and Quality Traits in Two Hybrid Rice Varieties (Oryza sativa L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 26;23(21):12934. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112934. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361748 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrogen and potassium interactions optimized asynchronous spikelet filling and increased grain yield of japonica rice.PeerJ. 2023 Jan 17;11:e14710. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14710. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36684678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai P, Bai R, Jin Y (2016) Characteristics and coordination of source-sink relationships in super hybrid rice. Open Life Sci 11: 470–475
-
- Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23: 2633–2635 - PubMed
-
- Cho JI, Lee SK, Ko S, Kim HK, Jun SH, Lee YH, Bhoo SH, Lee KW, An G, Hahn TR, et al. (2005) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of the cell-wall invertase gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep 24: 225–236 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

